Ethereum (ETH) is the leading smart contract platform powering DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 innovation. This 2025 guide explores Ethereum’s Proof-of-Stake consensus, dynamic tokenomics, Layer-2 scaling, and real-world use cases. Learn how ETH compares to Bitcoin, discover major updates like the Dencun and Pectra upgrades, and understand Ethereum’s investment potential.
Ethereum (ETH) Key Facts
-
Ticker Symbol: ETH
-
Blockchain Network: Ethereum Mainnet
-
Circulating Supply: ~120.7 million ETH (as of mid-2025)
-
Max Supply: Unlimited (no fixed cap; supply is managed via burns and PoS issuance)
-
Primary Use Case: Powering smart contracts and decentralized apps (DeFi, NFTs, Web3)
-
Current Market Cap: ~$320 billion (mid-2025)
-
Available on Phemex: Yes (trade ETH on Phemex spot and futures markets)
What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a blockchain platform designed for smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), with its native cryptocurrency being Ether (ETH). Launched in 2015, Ethereum introduced the idea of a "world computer," allowing developers to build versatile applications beyond basic digital payments. Vitalik Buterin and his co-founders proposed Ethereum in late 2013 to address the limitations of Bitcoin, which primarily focused on peer-to-peer transactions. After successful crowdfunding in 2014, the Ethereum network went live in July 2015, becoming the first widely adopted smart contract platform.
Ethereum solves several problems by expanding blockchain's utility. It introduced a Turing-complete programming language (Solidity) and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), enabling complex decentralized applications without needing a new blockchain. This innovation has led to the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and Web3 applications, allowing users to maintain control over their data.
Today, Ethereum is foundational for many DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and Web3 projects, solidifying its status as the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization and a key component of the crypto economy.
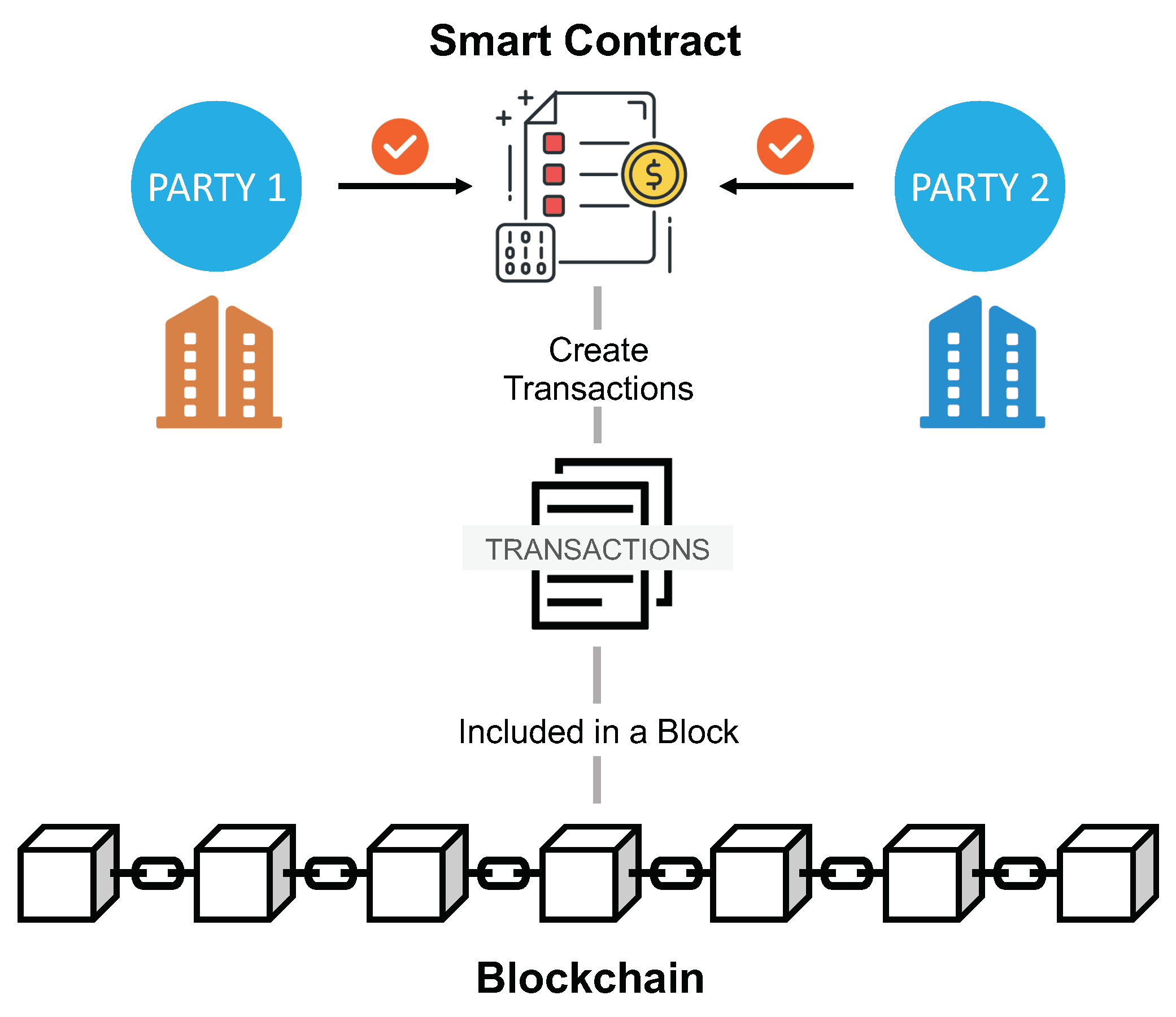
Smart Contract Workflow (source)
Ethereum Supply and Tokenomics
Ethereum's monetary policy diverges from Bitcoin's by not having a hard cap on supply; instead, it is managed dynamically through consensus rules. As of mid-2025, approximately 120.7 million ETH are circulating. While the supply can theoretically increase indefinitely, recent protocol changes, such as the fee-burning mechanism introduced in the August 2021 London hard fork, can lead to deflationary conditions. In this model, a portion of each transaction fee is burned, which can offset new coin issuance, leading to a net supply decrease during periods of high on-chain activity.
The September 2022 "Merge" upgrade transitioned Ethereum to Proof-of-Stake, reducing ETH issuance by over 90% due to the shift from mining rewards to staking rewards. In this new environment, the annual issuance rate dropped to around 0.5% or lower. Therefore, during high usage, ETH supply can shrink, while it can grow slowly during low activity. For instance, after high activity in early 2024, supply fell to about 120.07 million, then climbed to approximately 120.43 million by late November 2024, marking a mere 0.3% growth over eight months.
Ethereum's current tokenomics feature “minimal necessary inflation” with no fixed cap to ensure network security while incorporating fee burns to manage growth. Despite the recent Dencun upgrade in late 2024 causing ETH to become slightly inflationary again, supply growth remains under 1% per year. The dynamic supply model allows for potential deflation during high demand and mild inflation during quieter periods, aligning the interests of ETH holders with those of network users. Since the Merge, over 3 million ETH have been burned, offsetting much of the new issuance.
Ethereum’s Ecosystem and Use Cases
Ethereum’s versatility has fostered a vast ecosystem of use cases, making it far more than just a cryptocurrency. Here are some of the primary ways ETH and the Ethereum network are used:
Smart Contracts and dApps
Ethereum is primarily known for hosting smart contracts, which are self-executing codes on the blockchain. This functionality has led to thousands of decentralized applications (dApps), including decentralized finance services and NFT marketplaces. Users pay transaction gas fees in ETH to interact with these dApps, contributing to Ethereum's dominance in DeFi and NFT trading.
Gas Fees
Transactions on Ethereum require a gas fee, paid in gwei. These fees compensate validators and help prevent network spam. While gas fees can spike during high demand (like NFT drops), upgrades have aimed to stabilize costs. Gas is essential for Ethereum operations, creating consistent demand for ETH.
Staking (Proof-of-Stake)
With Ethereum's transition to Proof-of-Stake, users can stake ETH to become validators, securing the network and earning rewards. The minimum requirement to run a validator node can be costly, leading to staking pools and liquid staking solutions. The flexibility to withdraw staked ETH, introduced in the April 2023 Shanghai upgrade, has enhanced participation in staking.
Governance and Community
Ethereum's governance is community-driven and lacks formal on-chain voting. Changes are proposed through Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) and implemented with consensus among developers. While ETH holders don't vote directly on upgrades, they can influence changes by supporting specific software or forks.Integrations and Enterprise Use
Ethereum’s technology is widely integrated into various systems, with its smart contract standards (like ERC-20 for tokens and others for NFTs) becoming industry benchmarks. Many blockchains, including Binance Smart Chain and Polygon, are EVM-compatible, enhancing cross-chain compatibility and making it easier to port Ethereum dApps. The Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA), which includes companies like Microsoft and JPMorgan, is leveraging Ethereum for applications in supply chain tracking, trade finance, and decentralized identity. Additionally, leading stablecoins such as USDC and USDT operate on Ethereum, with PayPal’s USD stablecoin (PYUSD) launching on Ethereum in 2023.
Overall, Ethereum’s ecosystem is rich and continually expanding – from financial services and gaming to digital art and social media, Ethereum provides the programmable infrastructure powering the decentralized revolution.
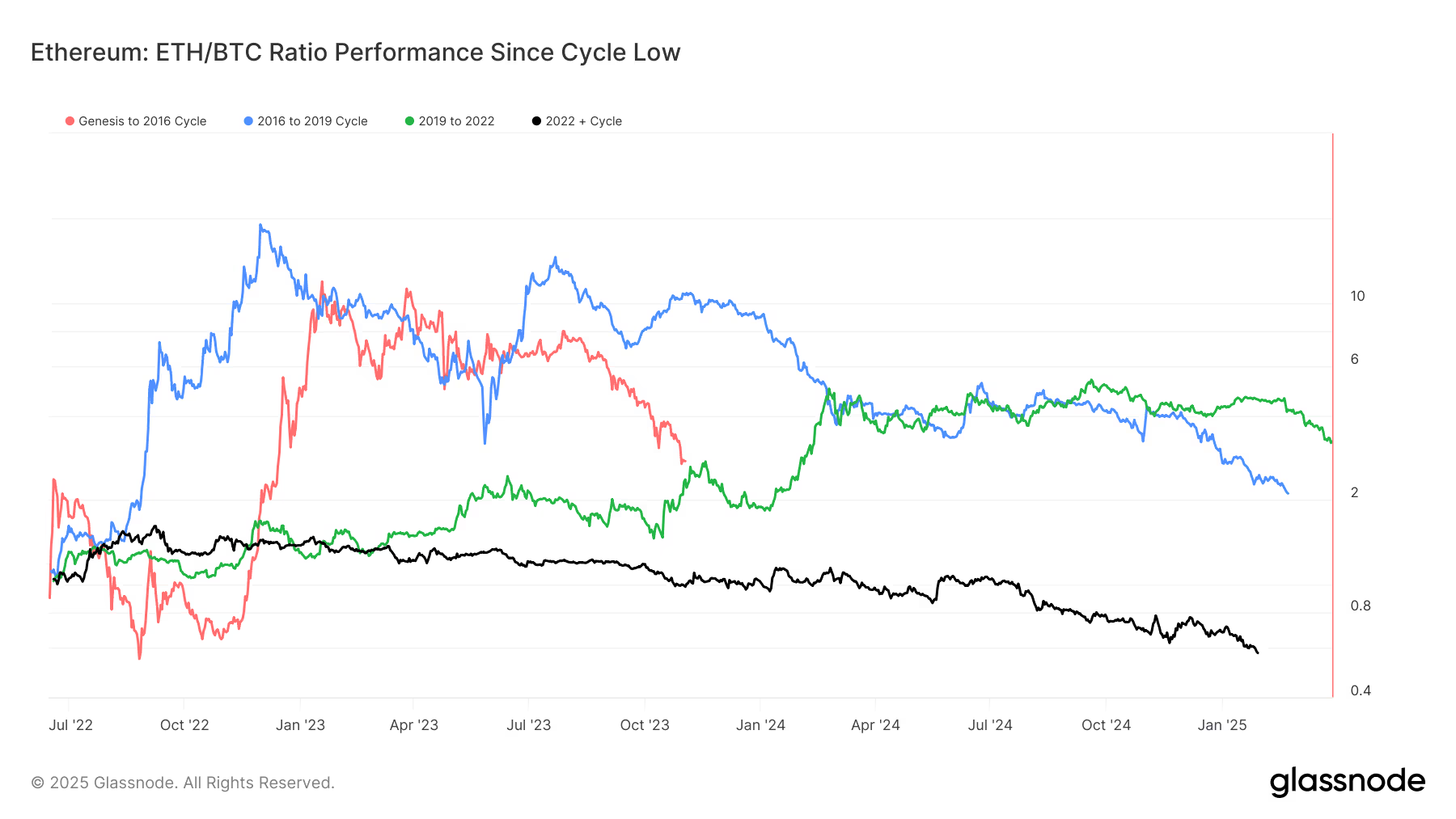
Bitcoin vs. Ethereum Performance (source)
Ethereum vs Bitcoin: Key Differences
Ethereum and Bitcoin are the two largest cryptocurrencies, but they have different goals and technical approaches:
Purpose and Use Case
Bitcoin serves primarily as digital money or "digital gold," designed for peer-to-peer cash transfers and as a store of value. In contrast, Ethereum is a decentralized application platform that enables smart contracts and dApps, functioning as a global computing platform. Bitcoin focuses on wealth storage and transfer, while Ethereum emphasizes programming and decentralized services.
Consensus Mechanism
Bitcoin uses Proof-of-Work (PoW) for security, relying on energy-intensive computations. Ethereum transitioned to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in 2022, utilizing validators who stake ETH, making it more energy-efficient. Both networks are considered secure, but Bitcoin’s PoW is more energy-intensive, while Ethereum’s PoS relies on economic staking.
Supply and Economics
Bitcoin has a fixed supply cap of 21 million BTC, making it deflationary over time. Ethereum lacks a preset max supply and historically has been inflationary. However, recent changes like fee burning have slowed ETH's supply growth, making it potentially deflationary. Bitcoin is viewed as a scarce asset, while Ether serves as a fuel for its network.
Transaction Speed and Throughput
Bitcoin produces blocks approximately every 10 minutes and handles about 5-7 transactions per second, while Ethereum produces blocks every 12 seconds, supporting 15-30 transactions per second. This makes Ethereum faster, suitable for activities requiring quick confirmations, while Bitcoin relies on Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network for scalability.
Fees
Bitcoin and Ethereum both incur transaction fees, but their structures differ. Bitcoin’s fees depend on block space demand and typically range from under $1 to $5-$20 during high activity. Ethereum’s fees are based on gas usage and can vary significantly; simple transfers may cost a few cents, while complex smart contracts can reach hundreds of dollars during congestion. Historically, Ethereum’s fees are higher on average than Bitcoin’s, but Layer-2 solutions are reducing costs for Ethereum users.
Flexibility
Bitcoin offers limited scripting capabilities, focusing on security and simplicity, making it unsuitable for sophisticated smart contracts. In contrast, Ethereum’s Turing-complete scripts support a wide range of applications, including token issuance and decentralized exchanges. However, this flexibility introduces potential security risks, such as bugs in smart contracts.
Decentralization
Both networks are decentralized but in different ways. Bitcoin relies on independent mining nodes and full nodes, while Ethereum uses validators in a PoS system. While Ethereum has a larger number of validators, concerns exist about centralization among staking pools. Bitcoin’s conservative development approach contrasts with Ethereum’s active upgrade schedule.
Security
Bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) has demonstrated resilience, requiring immense computational power to attack. Ethereum’s proof-of-stake (PoS) relies on economic penalties, making attacks costly. Although PoS is newer, it has proven effective since Ethereum's transition. Bitcoin’s simpler functionality reduces the risk of on-chain issues, while Ethereum faces potential smart contract vulnerabilities.
In summary, Bitcoin is often considered digital gold, optimized for value storage and secure transfers, whereas Ethereum is likened to digital oil, designed for transaction and application execution.
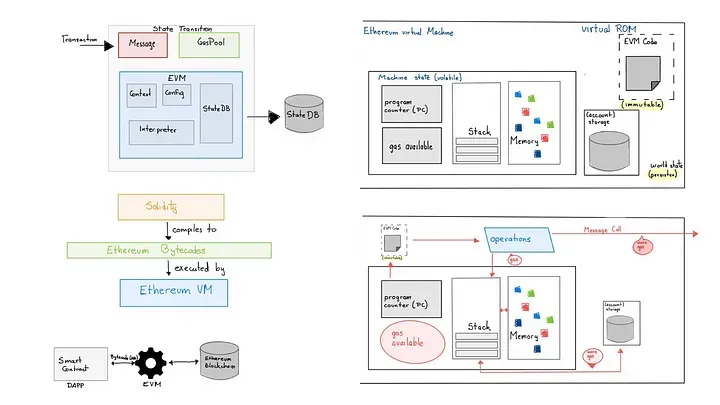
Ethereum Virtual Machine
How Ethereum Works: Proof-of-Stake and Scalability
Ethereum has evolved significantly, notably shifting from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) for consensus. In PoS, validators stake ETH as collateral and use validator software to create and validate blocks. Validators earn rewards for honest behavior, while malicious actions can lead to slashing. This PoS mechanism, called Gasper, finalizes blocks in epochs (~6.4 minutes) and substantially lowers energy consumption by over 99%. As of 2025, more than 34 million ETH are staked across over a million validators.
The Ethereum network features multiple execution (e.g., Geth, Besu) and consensus clients (e.g., Prysm, Lighthouse) to ensure resilience through code diversity. Transactions are executed in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), with smart contracts stored on-chain. Gas fees are required for computations, and upgrades like Verkle Trees are introduced to optimize data storage.
To address its limited transaction capacity (15-30 transactions per second), Ethereum employs Layer-2 rollups. These off-chain solutions compress transaction data and post it back to Ethereum's main layer, inheriting its security. The two main types are:
-
Optimistic Rollups (e.g., Optimism, Arbitrum) that assume validity unless challenged.
-
Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZK-Rollups) (e.g., zkSync, StarkNet) that provide validity proofs for off-chain transactions, allowing for near-instant finality.
Layer-2 solutions significantly boost Ethereum's throughput, enabling thousands of transactions per batch while reducing fees and speeding up processing. By 2025, most user transactions are expected to occur on Layer-2, with Ethereum Layer-1 serving as a security and data availability layer. The Dencun upgrade in late 2024 introduced protodanksharding, which provided cheaper data space for Layer-2s, resulting in a 4× increase in activity and a 99% drop in Layer-1 fees.
While rollups are the current scaling solution, Ethereum is also pursuing data sharding to enhance capacity. Sharding will likely focus on data availability rather than execution, with plans for full implementation in the coming years. The upcoming Pectra upgrade in 2025 will introduce features like Data Availability Sampling and Verkle Trees to further improve scalability.
Additionally, account abstraction is making Ethereum more user-friendly by allowing wallets to function like smart contracts, enabling users to pay gas fees with tokens other than ETH. This simplification aims to attract more mainstream users.
Ethereum's technology is also fostering partnerships with major companies and facilitating cross-chain integrations with ecosystems like Solana and Polygon. Overall, Ethereum’s ongoing innovations in scalability and usability ensure it remains a leading force in the crypto space, likened to a decentralized operating system.
Ethereum’s Founders and History
Ethereum was envisioned by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 when he was just 19. As a co-founder of Bitcoin Magazine, he published the Ethereum whitepaper, proposing a decentralized platform for various applications beyond financial transactions.
In early 2014, Buterin teamed up with co-founders Gavin Wood, Charles Hoskinson, Joseph Lubin, and others to launch Ethereum. They formalized the project in Zug, Switzerland, establishing it as a non-profit with an open-source ethos, supported by the Ethereum Foundation.
To fund development, Ethereum conducted one of the first Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) in mid-2014, raising about $18 million by selling ETH tokens in exchange for Bitcoin. The network launched its first version, Frontier, on July 30, 2015.
Ethereum experienced significant development phases, including Homestead (2016) and Metropolis (2017–2019), enhancing its functionality. A notable challenge was The DAO hack in June 2016, which led to a controversial hard fork. The majority continued on the new Ethereum chain, while the original chain became Ethereum Classic (ETC).
Initially relying on community funding, Ethereum later gained support from major tech firms through the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance. The Ethereum Foundation also received funding through its token holdings and donations, while venture capital began to invest in projects built on Ethereum, keeping the core protocol community-driven.
Timeline highlights:
-
2013: Vitalik conceives Ethereum, writes whitepaper.
-
2014: Ethereum co-founders assemble; crowd sale raises $18M; Ethereum Foundation established.
-
2015: Frontier (initial Ethereum network) launches.
-
2016: DAO hack and Ethereum/Ethereum Classic split; Homestead upgrade.
-
2017: ICO boom on Ethereum; ETH price surges from ~$8 to ~$700.
-
2018: Faced with scaling issues and competition, devs focus on upgrades amid a bear market.
-
2019: Metropolis phase ends with Constantinople and Istanbul upgrades, setting the stage for Ethereum 2.0.
-
2020: DeFi summer revitalizes Ethereum; Beacon Chain launches, marking the transition to Proof-of-Stake.
-
2021: NFT boom makes Ethereum the center of NFT trading; ETH price peaks around $4,800.
-
2022: Major bear market sees ETH drop below $1,000. The Merge transitions Ethereum to Proof-of-Stake, cutting energy usage by ~99.9%.
-
2023: Shanghai upgrade enables ETH withdrawals; layer-2 networks gain traction. The market begins recovering, with ETH price rebounding above $2,000.
-
2024: Dencun upgrade introduces proto-danksharding for scalability but ETH performs poorly compared to Bitcoin. Competition rises in NFTs and memecoins.
-
2025: Pectra upgrade planned focuses on validator performance. Ethereum's network fundamentals remain strong, with anticipation for a spot ETH ETF approval in the US.
Ethereum's journey from inception to a multi-hundred-billion dollar network underscores the power of community-driven, open-source development in the crypto space.
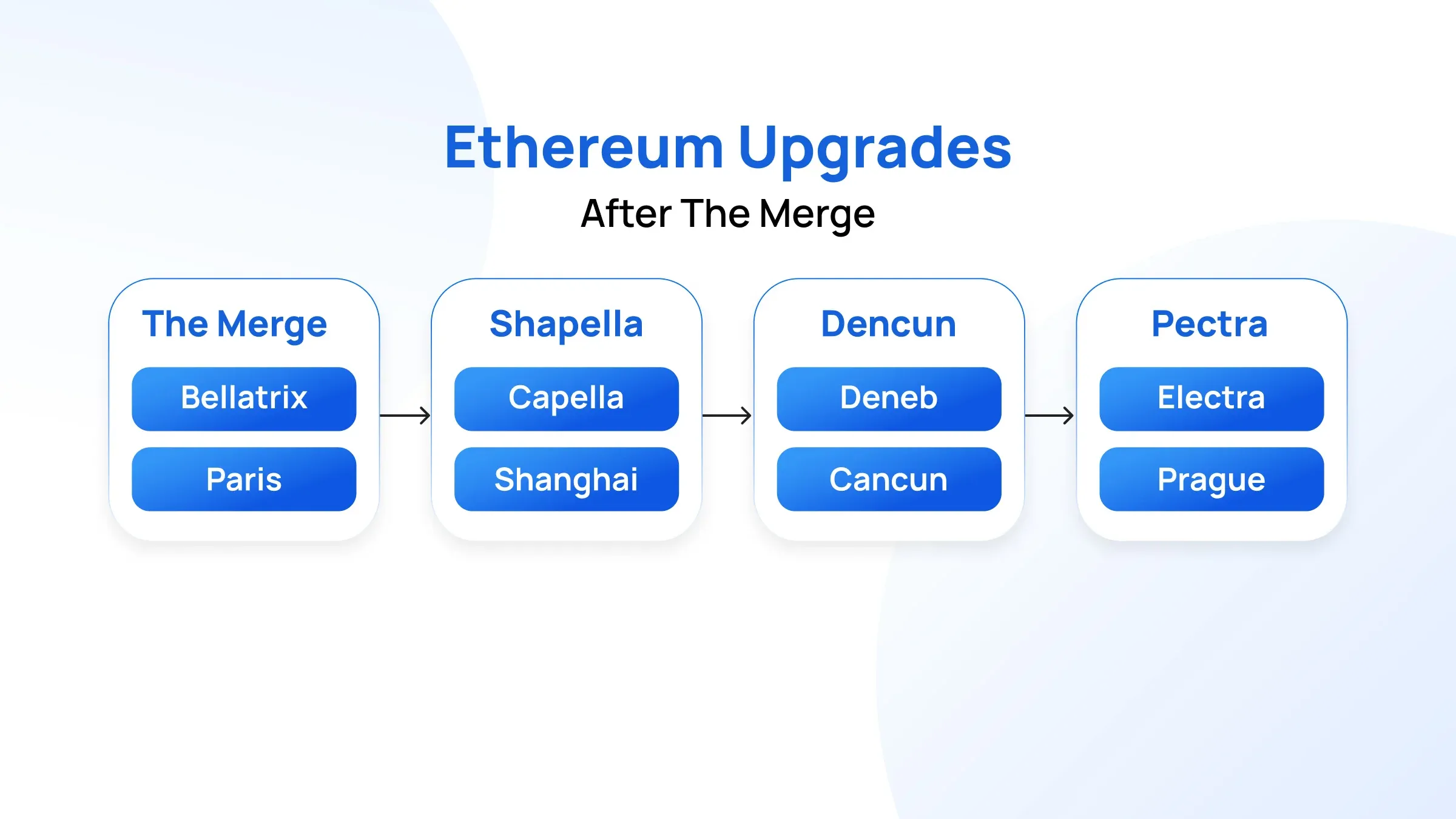
Ethereum Upgrades (source)
Recent Ethereum Developments (2024–2025)
The past two years have been eventful for Ethereum, with significant upgrades, regulatory developments, and ecosystem changes:
The Dencun Upgrade (2024)
The Dencun upgrade combined the Cancun and Deneb hard forks, introducing Proto-Danksharding, which allowed for data blobs that significantly reduced Layer-2 posting costs. This led to a dramatic drop in transaction fees on L2, resulting in a fourfold increase in rollup transaction volume. As a result, Ethereum’s Layer-1 experienced low fees, causing a slight inflationary period as ETH burn rates decreased. By early 2025, Ethereum's total supply had returned to approximately 120.52 million ETH, marking the first inflation since transitioning to Proof of Stake. The upgrade sparked discussions on long-term fee dynamics and security budget sustainability as L1 usage dipped; however, fees began to recover towards the end of 2024.
Regulatory and Legal Updates
Ethereum faced regulatory scrutiny in 2023-2024. While the SEC took actions against certain crypto services and labeled some tokens as securities, it did not classify ETH explicitly, contributing to its ongoing status as a commodity in many contexts. ETF-related developments were notable; by late 2023, the SEC approved Ethereum Futures ETFs, and by 2024, several spot ETH ETF proposals were anticipated.
Layer-2 Ecosystem Boom
2024 saw significant growth in Ethereum's Layer-2 ecosystem. Notable networks like Arbitrum and Optimism thrived, with Arbitrum launching a token and maintaining high transaction counts. Optimism introduced its "Superchain" for cross-chain collaboration. The Dencun upgrade's cost reductions bolstered L2 activity, establishing Ethereum's ecosystem as one of the most dynamic in crypto. Interoperability standards for L2s and improved cross-rollup transfers enhanced user experience significantly, making this period crucial for Ethereum's scalability.
Staking Developments
Following the Shanghai upgrade in 2023, which enabled withdrawals, staking participation rose significantly throughout 2024, reaching over 34 million ETH by March 2025. Liquid staking protocols like Lido and Rocket Pool grew, but centralization concerns emerged as Lido controlled about one-third of all staked ETH. The Pectra upgrade in 2025 increased the max validator balance to 2048 ETH, allowing larger operations to enhance efficiency and facilitating smoother validator exits.
Notable Partnerships and Integrations
In 2024 and early 2025, major endorsements for Ethereum technology surfaced. PayPal's PYUSD stablecoin saw increased use, while Visa's pilot for automatic payments via StarkNet showcased innovative uses of Ethereum. The trend of tokenizing real-world assets on Ethereum gained traction, indicating significant market potential. Starbucks and Reddit also integrated Ethereum technology, attracting more Web2 companies.
Market and Performance
After the 2022 bear market, Ethereum entered 2024 priced at around $1,200 and rallied throughout early 2024. By late 2024, ETH was up about 60% year-over-year. However, competition from newer L1s like Solana emerged. By early 2025, optimism returned, fueled by the successful Pectra implementation and potential developments, such as a Bitcoin halving and a possible Ether ETF approval.
In summary, 2024–2025 was marked by significant upgrades for Ethereum, enhancing its scalability and usability while facing competitive challenges and the need for greater user adoption.
Ethereum as an Investment: Potential and Risks (Not Financial Advice)
As the second-largest cryptocurrency, Ethereum (ETH) is a staple in many crypto portfolios. Its historical price performance has been volatile but notably strong over the long term. Early investors in the 2015 crowdsale saw ETH soar to over $1,400 in January 2018, drop to ~$80 during the 2018 bear market, and reach around $4,800 in November 2021. Over a 5-year span ending in 2024, ETH's price rose by approximately 20×, surpassing Bitcoin’s growth, but investors faced drawdowns of over 80%.
Owning ETH equates to having a stake in the Ethereum economy, as it’s needed for transaction fees, staking, and various DeFi and NFT activities. Increased usage can drive demand, while the burn mechanism may also positively affect value. Some analysts believe ETH could rival or surpass Bitcoin’s market cap, especially considering its potential yield from staking.
Ethereum thrives on a robust developer community, with more active developers than any other blockchain. This innovation fosters new projects and enhances ETH's utility. However, internal debates about scaling and security remain, but the community's ability to reach consensus on upgrades has demonstrated resilience.
Risks and Challenges: Despite the optimism, investing in Ethereum carries several risks:
-
Market Volatility: Ethereum (ETH) is subject to significant price fluctuations, often experiencing rapid 20-30% swings influenced by market sentiment, macroeconomic factors, and Bitcoin's movements. Investors should be prepared for high volatility and potential large drawdowns.
-
Technical Risk: Being a technology under active development, Ethereum may face critical bugs or smart contract hacks, which could undermine confidence and affect ETH's value. Complex upgrades like sharding also introduce risk if not executed properly.
-
Competition: Ethereum competes with other Layer-1 blockchains (e.g., Solana, Cardano) that may attract users with faster or cheaper options. Although Ethereum remains dominant in DeFi and NFTs, it's crucial to watch its market share as rivals gain traction.
-
Regulation: Regulatory changes can impact ETH’s usage and value. Heavy restrictions or classification as a security could dampen interest, although Ethereum is increasingly accepted within legal frameworks.
-
Liquidity and Market Dynamics: While Ethereum's market is generally liquid, crises can reduce liquidity, leading to exaggerated price moves, particularly if significant amounts of ETH are locked in DeFi.
Long-Term Outlook: Analysts are optimistic about Ethereum's role in Web3 innovation and potential growth areas like CBDCs and tokenized assets. Increased institutional interest and regulated investment products are promising signs, but investors should remain cautious and consider diversification. In conclusion, while Ethereum presents significant opportunities, potential risks should not be overlooked. Investing in crypto is highly speculative, and it's advisable to consult a financial advisor.
How to Trade Ethereum on Phemex
Trading Ethereum on Phemex is straightforward thanks to its user-friendly platform for both spot and futures trading. Here’s a concise guide to get started:
1. Sign Up and Verify: Create an account on Phemex using your email and password. Complete KYC verification for better limits and security, depending on your region.
2. Fund Your Account: Deposit cryptocurrency or fiat to trade ETH. You can transfer existing ETH or deposit stablecoins like USDT. Here is a guide on how to buy Ethereum on Phemex.
3. Choose Spot or Futures: For beginners, spot trading (buying/selling ETH directly) is easier. Find market pairs like ETH/USDT. If you prefer futures, Phemex offers perpetual contracts which allow leverage, but use caution.
4. Place an Order: On the trading interface, select your order type—market for instant buys/sells or limit for specifying a price. Review and confirm your order to add ETH to your wallet.
5. Using Phemex Tools: Take advantage of charts, indicators, and advanced order types for informed trading. Check for promotional bonuses that can enhance your experience.
6. Trade Responsibly: Define a trading strategy and never invest more than you can afford to lose. Start small if you’re new, and utilize risk management tools like stop-loss orders.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry inherent risks due to market volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and technological factors. Always conduct your own research and consult with a licensed financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Phemex does not endorse or guarantee the performance of any token or project.