Key Takeaways
Crypto staking allows users to earn passive income by locking up their crypto assets to support blockchain network operations like validation and security.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and its variants (e.g., Delegated PoS, Liquid PoS) are the foundation of staking, replacing the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work.
Liquid staking and restaking are rising trends in 2026, offering more flexibility and higher yields without locking assets long-term.
Ethereum’s transition to PoS and the rise of LSTs (Liquid Staking Tokens) have reshaped the staking landscape, making ETH the most staked asset globally.
Staking yields vary by protocol and depend on factors like inflation rates, validator uptime, and slashing risk.
Centralized exchanges (e.g., Phemex), DeFi platforms, and staking-as-a-service providers offer different risk-reward profiles for participants.
What is staking in crypto
Crypto staking is a way to help secure certain blockchains and earn rewards by committing (“staking”) tokens to the network’s consensus mechanism. On Proof-of-Stake networks, the participants who run validating infrastructure must typically lock some amount of the network’s native token as economic collateral. In return, the protocol can pay rewards to stakers who follow the rules.
The concept is often compared to “earning interest,” but it is not the same as a bank deposit. In staking, rewards are generated by the blockchain protocol and its economics (new token issuance and/or transaction fees), and staked assets can be exposed to protocol penalties (like slashing) and to operational and software risks. Traditional deposit protections generally do not apply to on-chain staking positions.
A key point for beginners: not every cryptocurrency can be staked. Staking is a feature of Proof-of-Stake consensus (and variants). Proof-of-Work assets don’t use staking for consensus, instead they rely on mining.
The practical reason staking exists is that Proof-of-Stake networks need a way to decide who gets to propose blocks and validate transactions without burning electricity to solve puzzles. The “stake” acts as a bond: if validators behave dishonestly, the protocol can punish them by destroying or reducing staked funds (slashing) and/or by withholding rewards.
Proof of Stake Consensus Algorithm
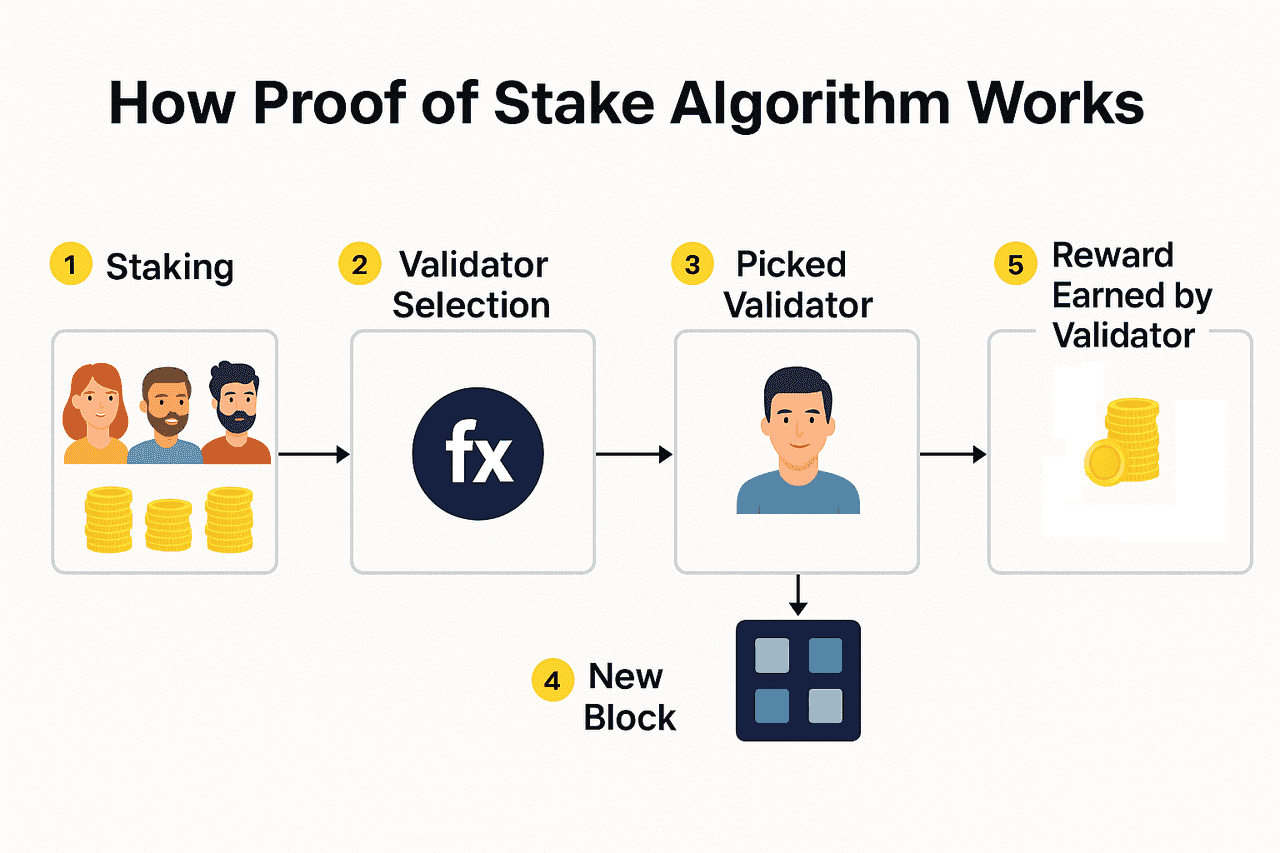
How Proof-of-Stake staking works under the hood
In Proof-of-Stake, a distributed set of computers called nodes maintains a shared record of transactions and state. The network’s protocol defines how validators are selected and how blocks are finalized. In general, Proof-of-Stake requires node operators to stake the network’s assets so they can be selected programmatically to validate blocks, with rewards consisting of newly minted tokens and a portion of transaction fees.
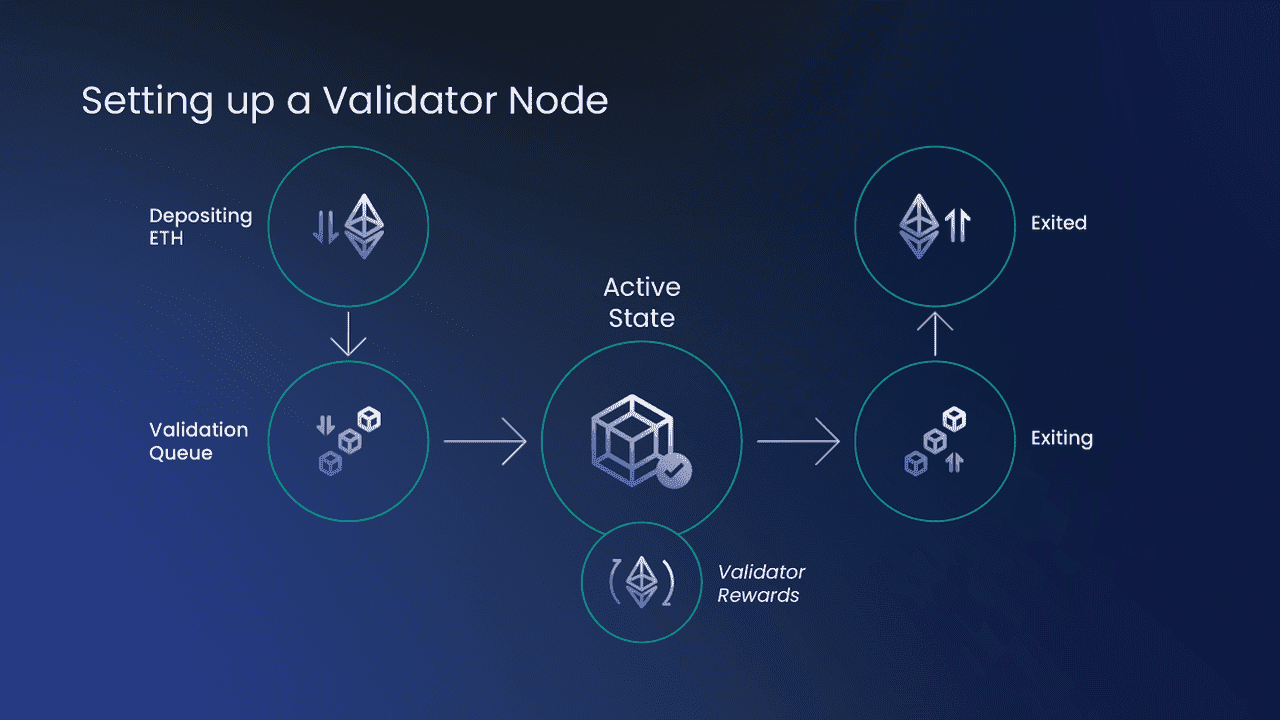
On Ethereum specifically, validators participate by depositing 32 ETH and running three pieces of software: an execution client, a consensus client, and a validator client. New validators enter an activation queue (which limits how fast the validator set can grow). Ethereum consensus operates in 12‑second slots grouped into epochs (32 slots). Each slot, one validator is pseudo-randomly selected as the proposer, and committees of validators attest to blocks.
Ethereum’s reward and penalty system is explicitly designed so that individual validator rewards depend on correct participation and how much total ETH is staked across the network. Rewards come from attestations, block proposals, and special duties like sync committees; penalties apply for missing duties, and serious misbehavior can trigger slashing and forced removal from the validator set.
Slashing on Ethereum is reserved for clearly dishonest behaviors (for example double-signing) and carries an immediate penalty plus additional penalties during a 36‑day removal period. Importantly, Ethereum penalizes correlated failures more heavily when many validators are slashed close together, increasing systemic risk for operators who run many validators with the same flawed setup.
Ethereum staking is also meaningfully “live” from a withdrawals perspective: the Shanghai/Capella upgrade enabled staking withdrawals (April 12, 2023), and partial withdrawals of rewards above 32 ETH are processed automatically to a withdrawal address. Full withdrawals occur after a validator exits and becomes withdrawable, with timing that depends on network dynamics.
Ethereum’s staking metrics and APR move over time based on network participation and fee activity. As displayed on Ethereum.org in late February 2026, the staking dashboard shows roughly 37M+ ETH staked, 960k+ validators, and a ~2.9% “current APR” figure (a snapshot estimate). These figures can change daily.
Other major Proof-of-Stake networks implement staking differently:
On Solana, token holders typically stake by delegating stake to validators. Validators charge a commission (a percentage of rewards), and delegation is framed as a shared‑risk shared‑reward model where more delegated stake generally results in a validator being selected more often to write transactions, increasing rewards for the validator and delegators. Solana’s documentation also notes that “in-protocol” slashing is not currently implemented, though it may exist in the future.
On Cardano, delegation is designed so ADA holders can delegate while retaining spending power, and rewards are distributed each epoch from a combination of transaction fees and monetary expansion. Cardano emphasizes “liquid” staking characteristics (no lock-up in the typical sense for delegators) and explains how pool performance and parameters influence rewards.
On Polkadot, staking includes bonding/unbonding concepts, slashing for misbehavior, and a notable unbonding period designed as a security mechanism to allow retroactive detection of slashable offenses. Polkadot also supports non-custodial nomination pools, enabling smaller holders to stake natively with low minimums (the wiki cites “as little as 1 DOT” for rewards eligibility via pools, depending on pool activity and system limits).
Across networks, the shared economic idea is the same: staking aligns incentives by requiring validators to have “skin in the game.” But the user experience differs a lot: some chains are effectively liquid for delegators (you can move funds freely), while others enforce strict unbonding periods where funds stop earning rewards and remain illiquid for days or weeks.
Register on Phemex to Stake PT
Validator Nodes on Ethereum
Ways to stake crypto in 2026
Native staking
Native staking means participating using the chain’s built-in staking mechanism, directly with the protocol rules.
For Ethereum, “native” can mean solo staking (you run your own validator) or using mechanisms that keep withdrawal control with you. Ethereum.org classifies options across home staking, staking-as-a-service, pooled staking (including liquid staking providers), and centralized exchanges—each with different trust assumptions and risk profiles.
For Solana, native staking is generally delegation via wallets that create and manage stake accounts, choose validators, and delegate stake. The docs call out the validator commission and explicitly advise delegators to do their own due diligence.
For Cardano, “native staking” is usually delegation to stake pools, where spending power is retained and epoch rewards flow based on the protocol’s reward calculation and pool performance.
Delegated staking and staking pools
Many Proof-of-Stake networks allow token holders to delegate to validators rather than run validator infrastructure. This expands participation but introduces validator selection risk because you’re trusting the validator’s uptime and behavior.
Some protocols apply slashing to delegators if the chosen validator is slashed. For example, Polkadot’s nominators must monitor whether their stake is actually backing an active validator set to receive rewards and to manage misbehavior risk. Nomination pools reduce the practical complexity but still involve protocol-level slashing exposure when active validators misbehave.
Custodial staking
Custodial staking is when you deposit assets with a third party that controls the wallet and stakes on your behalf. A common reason users choose this route is convenience, but it adds counterparty and custody risk. When users hand over tokens to a staking-as-a-service provider, they lose control and take platform risks “with very little protection,” and the provider can market returns and manage the staking strategy.
Liquid staking
Liquid staking is a hybrid: your underlying assets are staked, and you receive a staking receipt token that represents your staked position plus accrued rewards. This is popular because it can preserve liquidity as users can potentially trade the receipt token or use it in DeFi while still earning staking rewards.
A key real-world detail: liquid receipt tokens are not necessarily pegged to the underlying asset 1:1 in market price. For example, Lido explicitly notes that stETH is not intended to be pegged to ETH and secondary-market pricing can differ based on supply and demand. Selling on secondary markets can provide instant liquidity but can involve price slippage versus redeeming through the protocol queue.
Liquid staking also introduces new risk categories: smart contract risk (the protocol contracts), oracle/accounting risks, and depeg / liquidity risk in stressed market conditions if users try to exit at the same time. Even when protocols have redemption queues, exit times can grow during congestion.
Restaking and liquid restaking
Restaking is an additional layer where staked assets are reused to secure other services, potentially earning extra rewards at the cost of additional slashing conditions and complexity.
In the Ethereum ecosystem, restaking has largely been associated with EigenLayer. EigenLayer describes liquid restaking as depositing liquid tokens such as liquid staking tokens and other supported assets into EigenLayer smart contracts, and native restaking as modifying an Ethereum validator’s withdrawal credentials to point to EigenLayer smart contracts. It also emphasizes that restakers delegate to a single operator at a time, and that delegation is “all or nothing” for the available restaked balance.
Most importantly for risk: EigenLayer warns that delegated stake can become slashable when an operator opts into operator sets and allocates “Unique Stake,” and that some operator sets can be “redistributable,” increasing incentives to slash and raising the risk profile. Compromised AVS governance or slashing logic could allow an attacker to drain delegated funds, and that slashed funds may be burned or redistributed depending on the configuration.
From a product perspective, restaking is best treated as an advanced staking strategy rather than a default choice for beginners, because each additional layer increases dependency chains, attack surface area, and correlated cascade risk.
Staking rewards explained: where APY comes from and how to compare offers
Staking rewards are not magic. They are shaped by protocol economics and execution details.
Reward sources
Two core reward sources are common in PoS systems: (1) newly minted tokens distributed by protocol rules and (2) a share of transaction fees paid by users submitting transactions.
In the Ethereum ecosystem users pay both a base fee and a tip - tips are paid to validators, while the base fee is burned. Validators can also earn additional value through block proposal opportunities (including MEV-related dynamics), which can make realized rewards for some validators higher than simple “base APR” estimates.
Cardano describes epoch rewards as coming from all transaction fees plus a monetary expansion component drawn from reserves, then adjusted by stake pool performance and distributed after subtracting operator costs and margins.
Solana frames staking rewards as linked to how often a validator is chosen to write transactions, minus validator commission, with the protocol noting commission competition and advising stakers to choose validators carefully.
Why yields change over time
Even in simple PoS models, APR changes because:
More total stake usually means per-validator rewards decrease, because the reward formula spreads issuance across more participants. Ethereum explicitly describes base reward as inversely related to the size of the active validator set and total active balance.
Transaction fee activity changes daily, affecting fee-derived rewards.
Validator performance (uptime, correct signing, inclusion delay) directly impacts outcomes because missed duties reduce rewards and, on many networks, can generate penalties.
Some networks impose bonding/activation delays and unbonding periods, affecting when you start earning and when you can exit.
Why “staking APY” advertisements can be misleading
Staking rewards are probabilistic and policy-driven. They are also sensitive to fees and middlemen.
Validators or staking providers can charge commissions/fees that reduce your net yield
Liquid staking adds market-price risk: even if protocol redemption is available, secondary-market pricing may differ from underlying value during volatility, affecting realized outcomes if you sell to exit quickly.
A practical investor mindset: treat staking yield as a variable stream that depends on protocol rules + validator performance + fees + (sometimes) market structure like MEV.
For example, Ethereum’s roadmap research on proposer-builder separation (PBS) explicitly frames MEV as a centralizing force because sophisticated actors can extract more value—potentially pushing returns toward large operators. PBS aims to route MEV rewards to proposers and validators even if specialized builders dominate extraction, to reduce the centralizing pressure and improve reward distribution for home stakers.
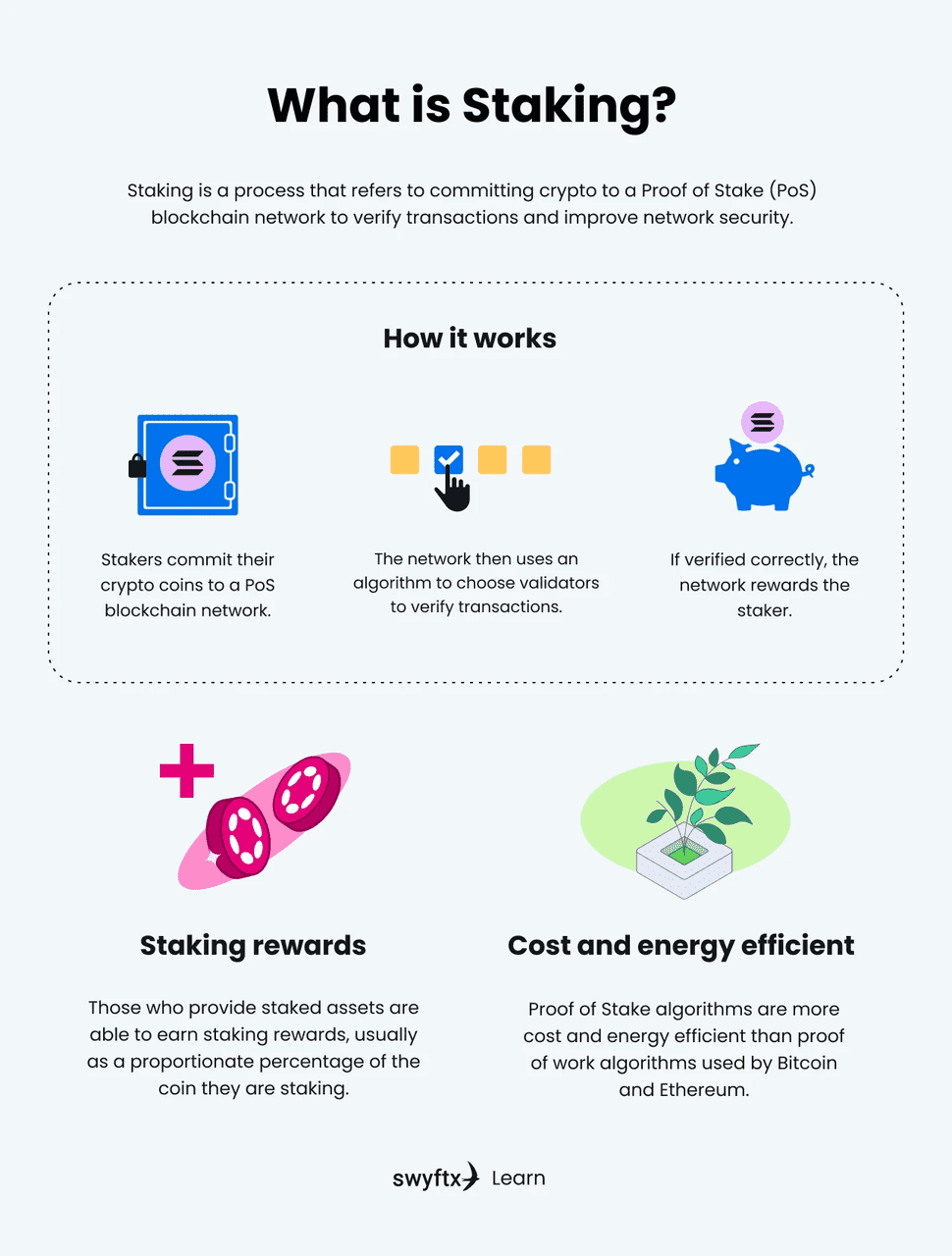
What is Crypto Staking (source)
Staking risks in 2026 and how to manage them
Staking can be a productive long-term strategy, but it is not “risk-free passive income.” Here are the main risk classes that matter in 2026.
Slashing and protocol penalties
Slashing is the most direct way a staker can lose principal due to validator misbehavior. Ethereum’s slashing rules include immediate burning plus additional penalties during forced exit, and penalties can scale up during correlated slashing events.
Other networks also have slashing, often extending risk to delegators. For example, Cosmos-focused documentation notes that delegators can be slashed if a validator violates rules, and that assets can remain slashable even during a 21‑day unbonding period.
Polkadot highlights slashing as a con of staking and positions its unbonding period as a security feature by helping ensure slashable offenses discovered from past eras can still be applied.
Solana’s official staking reference currently states that slashing is not implemented in-protocol today, but could exist in the future. This is an example of why staking rules must be reviewed per-chain and updated as networks evolve.
Lockups, unbonding, and liquidity constraints
Depending on the chain, unbonding can be hours, days, or weeks. During unbonding, you may stop earning rewards and you may still be exposed to slashing in some designs.
For Ethereum, even after withdrawals were enabled in 2023, exit timing can still vary because exiting requires a voluntary exit and then network processing including exit-rate limits and sweep mechanics. Ethereum emphasizes that reward withdrawals are automatic once credentials are set, but full exits require the validator exit and sweep process, which depends on network conditions.
Liquid staking can reduce lockup pain but introduces market dynamics: protocol redemption queues can take time, while secondary-market exits can be instant but may be at a discount or premium depending on conditions. Lido’s docs describe both routes and warn that stETH is not intended to maintain a fixed peg to ETH.
Smart contract and oracle risk
Native staking at the protocol level generally avoids third-party smart contract dependencies . Liquid staking and restaking, by design, rely on additional smart contracts that can be exploited or mis-specified.
For example, EigenLayer’s documentation is unusually explicit about systemic and governance risks: it warns that malicious AVSs or compromised slashing functionality could drain operator-delegated funds, and that redistributable operator sets can increase incentives to slash, raising risk.
Custody and counterparty risk
If you stake through a custodial intermediary, your risk profile changes:
You are exposed to the custodian’s operational security and solvency risks.
You may be subject to contracts, terms of service, and jurisdictional enforcement actions.
You can face limitations on withdrawals, especially during platform stress.
A practical staking safety checklist
A reasonable safety posture in 2026 is to treat staking like operating a “mini financial system”: you manage keys, software rules, counterparties, and tax records.
A minimal checklist for most users includes: (1) understanding the chain’s bonding/unbonding and slashing rules, (2) choosing validators/providers with transparent fees and strong operational track records, (3) avoiding concentration in a single operator or single strategy, and (4) keeping records of reward receipts for tax reporting. This aligns with protocol documentation emphasizing due diligence and monitoring.
Staking FAQ and glossary
Staking terminology can feel overwhelming, so here are the most useful “working definitions” in 2026.
Validator: A participant (person or organization) running software that proposes blocks and/or attests to blocks (varies by chain). On Ethereum, validators propose blocks and attest; missing duties reduces rewards, and dishonest actions can be slashed.
Delegator: A token holder who delegates stake to a validator, typically earning a share of rewards while taking some risk tied to validator performance and (in many networks) slashing exposure.
Staking pool: A mechanism that aggregates stake from multiple holders so they can participate in staking more efficiently. Pools can be protocol-native (e.g., Polkadot nomination pools) or third-party. Pools often simplify participation but can introduce additional risks and fees.
Bonding / activation period: A delay before staked assets become eligible to earn rewards (varies by protocol). Bonding periods and unbonding periods can range from hours to weeks, depending on the protocol.
Unbonding period: The time it takes to unstake assets and regain liquidity. Some networks keep assets exposed to slashing during unbonding; some do not.
Slashing: A penalty mechanism in many PoS systems that destroys or deducts staked assets after provable misbehavior. Ethereum has explicit slashing conditions and a forced exit process; Polkadot and Cosmos also support slashing in their staking models.
Liquid staking: Staking via a provider that issues a receipt token representing ownership of the staked position and accrued rewards.
Restaking: Reusing staked assets to secure additional services and earn extra rewards, typically by accepting additional slashing conditions. EigenLayer’s documentation emphasizes that delegated stake can become slashable as operators allocate specific stake to operator sets (including redistributable sets), and that governance compromise can create severe risks.
MEV: Maximum extractable value—profit validators can earn by ordering transactions favorably. Ethereum’s PBS roadmap notes MEV can centralize returns by favoring sophisticated operators, and describes PBS as an approach to route MEV rewards to proposers rather than requiring every validator to run complex MEV tech.
Final Note
Staking can be a powerful way to participate in Proof-of-Stake networks and potentially earn rewards, but the right approach depends on your risk tolerance, time horizon, liquidity needs, and operational competence. Protocol rules, slashing exposure, and regulatory/tax obligations have all evolved materially since 2023 and they continue to evolve through February 2026.