Summary:
-
Circulating supply (the number of coins in circulation) and total supply (the maximum number of coins that can exist) are key determinants of a coin’s price.
-
If a coin’s circulating supply is very far off from its total supply, there is a real dilution risk, because the moment more coins are added to circulation, its value will decrease, especially if fresh demand doesn’t come in to prop up the price.
Quick example: Bitcoin (BTC) has a circulating supply of about 19.4 million in mid-2025, with a total (max) supply of 21 million. That means ~92% of all BTC that will ever exist are already in circulation. On the other hand, a newer altcoin like Aptos (APT) might have, say, 200 million tokens circulating out of a 1 billion total supply – only 20% in circulation. This discrepancy signals that APT has a lot of tokens that could enter the market in the future, potentially diluting its price if demand doesn’t grow. Understanding such differences can be the difference between profits and painful losses in crypto investing.

Investing in crypto successfully requires due diligence that starts with fundamental research. One of the fundamental analysis components that all traders should look at is the circulating supply and the total supply of a coin.
What happens if you buy a coin with a circulating supply of one million, only to see the supply increase to five million, diluting your share by 500%? The tokenomics can make or break a crypto project because they are directly tied to market cap.
If the circulating supply increases, there has to be an influx in cash to retain the market cap. The more coins are added to circulation, the more the value decreases. Conversely, the more coins are burned or removed from circulation, the more the value increases.
This guide will analyze how circulating supply affects crypto prices and what to research in a project. We will also break down examples of the world’s biggest cryptos. By the end of this article, you will know exactly what to look out for in your next crypto investment–at least in regards to circulating supply and total supply.
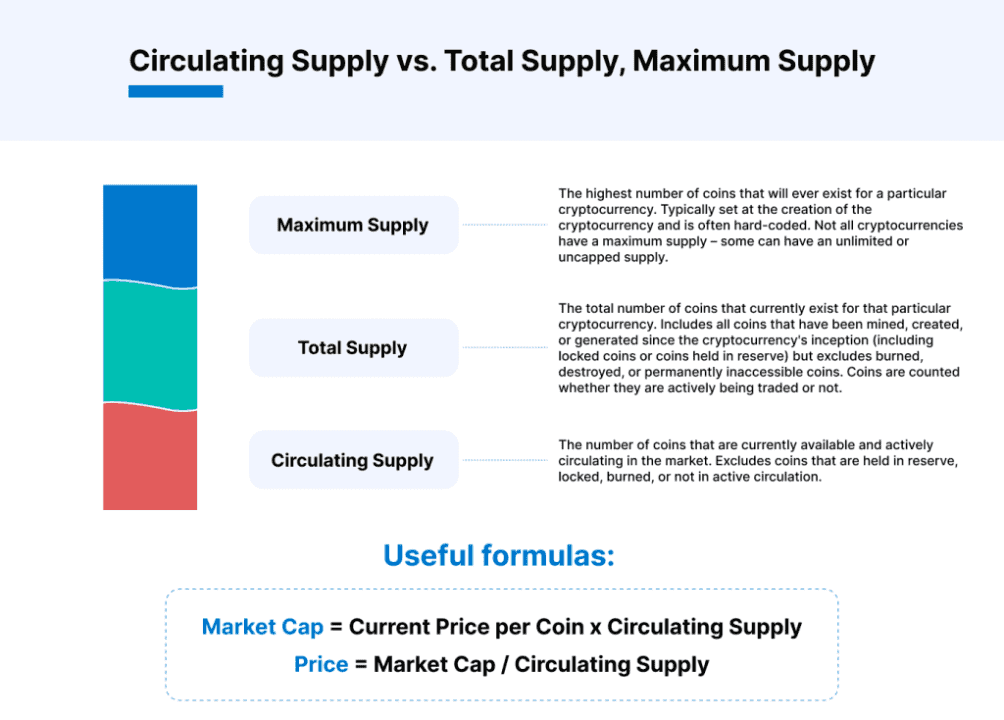
What Is Circulating Supply?
The circulating supply is the current number of coins that circulate on the blockchain. For Bitcoin, the circulating supply is 19 million and for Ethereum the circulating supply is 121 million.
The circulating supply is always a percentage of the total supply – the higher the percentage, the better. For example, Bitcoin has a circulating supply of 19 million, which is about 90% of the maximum supply of 21 million. This means that Bitcoin’s value can’t be significantly diluted by a deluge of new bitcoins coming into the market.
If the circulating supply is five million and the total supply is 100 million, this means the circulating supply is effectively 5%. This is risky; a holder could be looking at a dilution rate of 95% if they fail to do their research prior to investing.
How to Calculate Circulating Supply?
The circulating supply can be calculated by dividing the market cap by the coin price. The formula is the following:
-
Market Cap / Price = Circulating Supply
For Bitcoin, the $380 billion market cap can be divided by the $20,000 price, producing a result of 19 million BTC.
How to Calculate Market Cap?
The opposite applies if we want to calculate the market cap (total value) by multiplying the circulating supply by the coin price.
-
Bitcoin’s circulating supply is 19 million; multiplied by $20,000, the market cap is roughly $380 billion.
-
Ethereum’s circulating supply is 121 million; multiplied by $1,150 the market cap is roughly $140 billion.
-
Dogecoin’s circulating supply is 132 billion; multiplied by $0.07 the market cap is roughly $9 billion.
-
Chainlink’s circulating supply is 470 million; multiplied by $6.4 the market cap is roughly $3 billion.
Using a market cap and circulating supply calculator such as CoinMarketCap, the market cap calculation is processed automatically.
How Does Circulating Supply Affect Cryptocurrency Price?
Many novice traders assume that just because the price of a crypto is high, it must mean that the project is superior. This may not be the case; it could just mean that the circulating supply is low for now.
Ethereum’s circulating supply is nearly six times higher than that of Bitcoin’s, which is why the price is lower at $1,200 per ETH while Bitcoin is trading at $20,000 per BTC.
The converse is true; just because the price of a crypto is low, it does not automatically mean it’s an inferior project, because the supply might be high. In fact, it may well be a top 20 crypto by market cap.
A great example is Shiba Inu. With a circulating supply of 550 billion, it has a price of $0.0001 per coin. Despite that, the market cap is still relatively high at $6 billion.
What Is The Total Supply?
The total supply is the maximum amount of coins and represents a limit that cannot be exceeded. The total supply of any crypto is hard-coded in the code, and further mining is not allowed.
For example, Bitcoin’s total supply is 21 million. Bitcoin inflates at a rate of 6 BTC per block at the moment (every 10 minutes), but as the rewards decrease with halvings, the total supply is expected to be only fully mined in 100 years.
Circulating Supply vs Total Supply
Circulating supply is different from total supply because it calculates all coins that are active on the blockchain. Bitcoin’s founder, Satoshi Nakamoto, holds over 1 million BTC, equivalent to $20 billion at the current market. Those coins haven’t been moved in over 10 years, but they are still considered part of the circulating supply.
A sudden increase in total supply can cause significant damage to a project.
The Terra (LUNA) collapse is one example. To re-peg the algorithmic stablecoin UST, the Terra team had to mint new LUNA to back the liquidity of the UST stablecoin. The total supply of LUNA increased from 300 million up to 6.5 trillion in a matter of days. The price went down from $80 down to $0.0001–a fraction of a cent due to the rapid increase in supply, devaluing the project.
This risk is not likely in the case of Bitcoin, as the inflation rate is spread out over 100+ years. The risk of inflation is higher for DeFi coins powered by smart contracts, especially with minting bugs causing the majority of hacks in the DeFi scene.
Dilution Risk: Beware When Circulating Supply Is Far Below Total Supply
Consider a token, "XYZ," with a total supply of 1 billion but only 100 million in circulation at launch, priced at $1. If 900 million unlocks over three years with no demand increase, the price could fall significantly. A project can maintain or even grow its market cap while token prices decline due to increased supply, illustrating the importance of ensuring that adoption growth outpaces supply growth for price appreciation.
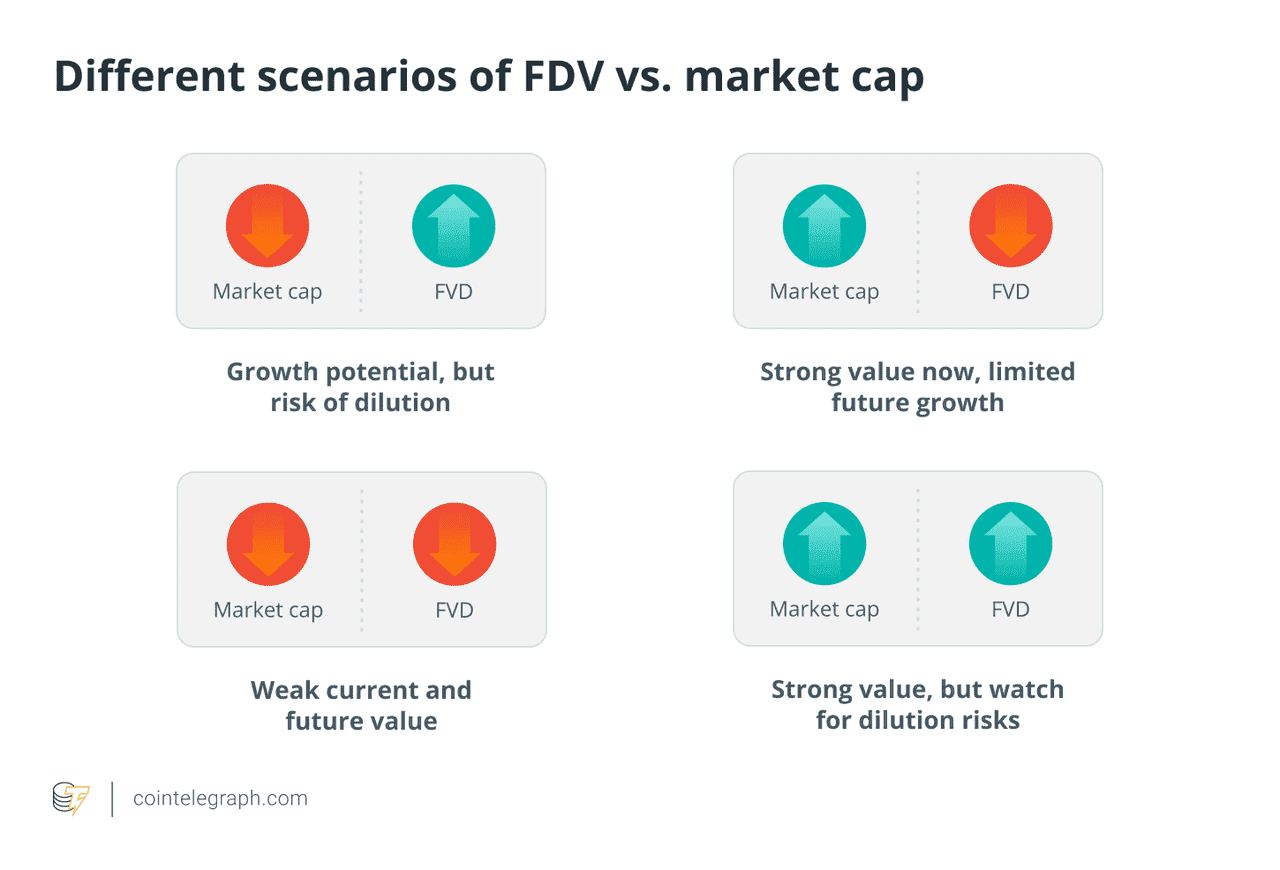
How to Assess a Project's Supply and Manage Dilution Risk
For an investor or trader:
-
Read the whitepaper or tokenomics docs: They usually outline initial distribution and unlock schedule. Look for tables or charts that show circulating supply over time.
-
Use tracking tools: Websites like Messari or CoinGecko often have tokenomics sections. There are also dedicated “token unlock calendar” sites now.
-
Consider the use of locked tokens: If team tokens are locked but the team is strong and unlikely to dump, maybe risk is less – or if they’ve communicated plans like “team won’t sell, or will extend lock”. But one must take such promises with a grain of salt.
-
Diversify timing: If you love a project but know dilution is coming, one strategy is to scale in slowly or wait until after major unlock events to buy more. Let early sellers exit.
-
Stake or earn yield if possible: If a project is inflationary but offers staking that yields the inflation, by staking you maintain your relative share. For example, if a coin inflates 5% a year but you can stake and earn 5%, you keep up with the new supply (assuming price impact aside). Many people stake to mitigate dilution.
-
Monitor on-chain metrics: Are new tokens being absorbed by new users (addresses growing, on-chain volume up)? If yes, maybe demand is matching supply, which could stabilize price.
How Does Burning Decrease Circulating Supply?
Coin burning can cause a jump in price for existing coins because fewer coins are in circulation. The act of burning represents the removal of coins from circulation by sending them to the burn address.
The “burn address” is the first genesis address on a blockchain. The burn address is where coins are sent if they want to be removed from circulation because no one has the private keys and they can’t be retrieved.
Upon sending to a burn address, block explorers such as Etherscan detect a decrease in supply, which is then typically reflected in a price increase. This is how projects such as Shiba Inu decreased their supply significantly and made their project successful.
What Happens When Circulating Supply Reaches Max Supply?
If the circulating supply and the max supply are equal, this means all coins were released in circulation. The crypto price could go up or down depending on market conditions, but nothing drastic will happen.
For example, the Litecoin circulating supply and maximum supply are identical at 84 million, meaning all LTC were mined. The price of Litecoin fluctuates based on market conditions. During the bull market in 2021, LTC reached an all-time high of $386 and then gradually decreased to $50 in the bear market.
How To Make Investment Decisions Based On Circulating Supply?
To successfully invest in crypto, one must research the ratio between the circulating and total supply. If more than 80% of coins are released in circulation, there is limited dilution coming down the pipeline. If less than 50% of coins are released in circulation, an investor risks dilution and a price drop.
If the circulating supply increases, the market cap doesn’t always follow. Let’s say we double the Bitcoin supply to 42 million. The market cap might remain the same at $380 billion, but the price of Bitcoin could decrease to $10,000 unless there is 2x the amount of cash injected to retain the current market cap.
One rule of thumb can be to ensure that the project you’ve invested in does not have less than 50% of the supply in circulation. While the price might appreciate in the short-term, dilution can slash potential gains over the next few years.
Conclusion
Circulating supply vs total supply is not just a dry statistic; it’s a lens through which you gauge a crypto’s future supply pressure. A coin can have great tech and adoption prospects, but if its tokenomics floods the market with new tokens, investors might not see gains. Conversely, a coin with strong tokenomics (high circulating %, deflationary or low inflation) can sometimes surprise people with price resilience or growth even on moderate demand.
For anyone stepping into crypto in 2025, always do the math on supply. The crypto world has matured to the point where these metrics are widely available so ignore them at your peril. In the end, knowledge of token supply helps you avoid being diluted out of profits and allows you to strategically position yourself in projects that offer not just a great vision, but also a sustainable economic design for their token.