With the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), many platforms are emerging with an eye to taking the decentralized digital currency throne. Locked in competition with each other, these platforms, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), are in a virtual “arms-race” to see who can create the most stable platform, with the most features, and the most user-friendly interface. One entity with such hopes and aspirations is Mango Markets.

What Is Mango Markets (MNGO)?
Mango Markets is an emerging and decentralized cross-trading platform for cryptocurrencies. But what does this mean, exactly? A cross-trading platform is where a user can take earnings from one transaction and use it to place orders for another, without needing to exit the first order. This practice is commonly used to help manage or offset the risk of the first transaction. Here’s a very simple example of a cross-trade, for reference:
- Yesterday, Bitcoin (BTC) was trading at $7,000 a coin. Since you had the capital, you decided to invest.
- Today, BTC is trading at $8,000 a coin. You decide to sell $1,000 worth of your BTC.
- Instead of pocketing that profit, you immediately buy 3 Mango Tokens (MNGO) (let’s say MNGO is valued at $330 a token).
- You have retained your original $7,000 worth of BTC, and now have 3 MNGO as well.
- You have just performed a cross trade.
In the case of cross trades, no record of individual transactions is kept on the exchange; instead being recorded as one single “cross trade.” It is for this reason, and the security concerns that arise from it, that cross-trading is not permitted by most major exchanges.
Through its use of the Solana blockchain, Mango Markets allows for up to 5x leverage (or margin) for its clients. This permits an investor to buy more stock/assets than their capital would usually allow. So, if they have $10 at 5x leverage, they can operate as if they had $50. Additionally, it is Mango’s use of Solana’s framework that allows it to boast surprisingly low-latency for its transaction speed; a feature which is appealing to most crypto-investors. Latency in this case refers to the time taken between a transaction being submitted by a user, and the blockchain network accepting that transaction.
Mango Markets’ stated goal is to create a user-friendly decentralized trading platform which offers advantages for both market “takers” and market “makers” alike. Market takers are crypto-asset buyers prepared to pay the going rate for a digital currency, while market makers are buyers who are waiting for a lower rate than the current one offered. Eventually, Mango Markets intends for its platform to reach a point where it challenges centralized exchanges in trading volume.
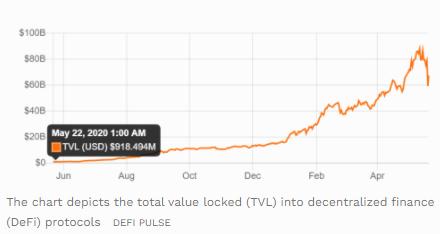
This objective may seem overly ambitious to many, if perhaps not to the team behind Mango Markets themselves. However, the ever-expanding world of DeFi has opened the eyes of potential investors and innovators to the many possibilities this sector has to offer worldwide. Thus, with decentralization being the key focus of many investors, the thought is that perhaps a decentralized platform like Mango Markets could someday overtake more classic forms of centralized finance (CeFi).

How Is Mango Markets Structured?
Since its inception in 2021, Mango Markets has built its brand by offering low transaction costs, full decentralization, and most importantly, low latency for said transactions to its users. Through this offering, Mango Markets can reduce the risk of slippage, or losses incurred by response delays (such as those brought about by latency). This allows its users to trade with less worry, and more liquidity. Mango Markets achieved this through its various building blocks:
- Solana Blockchain: Solana is a high-speed, open source blockchain with a rapidly rising reputation in the world of decentralized digital finance. By using Solana, Mango Markets aims to achieve high transaction speeds, but low transaction costs, all without infringing on their reputation as a decentralized network. Solana’s native cryptocurrency is the altcoin SOL, which is one of the cryptocurrencies traded on the Mango interface.
- Serum DEX: Also built on the Solana blockchain, Serum DEX offers Mango Markets users the opportunity to margin trade by using their permissionless, central limit order book (CLOB). This is a method of exchange secured by matching the price (amount) and time (moment executed) of a transaction; allowing users to trade and validate trades with each other directly, instead of needing an intermediary. Additionally, by being permissionless, Serum DEX’s transparency is further increased; as this invites anyone to download and participate in verifying information in its digital record. Serum DEX gives Mango Markets’ clients the ability to trade with 5x leverage, and up to 10x leverage for perpetual futures markets.
- Mango Token (MNGO): MNGO is the native altcoin used and exchanged by Mango Markets. It is primarily a governance token, meaning that MNGO owners can participate in making decisions on the protocol itself, and even impact wholesale system changes in some extreme cases. This gives users greater control over the platform and ties in with Mango Markets’ claims of being a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
By using Solana’s blockchain, Mango Markets hopes to eventually achieve latency delays of just 400 milliseconds, which is close to industry-leading speed. However, it is important to note that crypto price/data fluctuations can be subject to change within a fraction of that time. This means that even with lightning-fast exchanges like Mango Markets, investors can lose money should the market suddenly swing out of favor (even when in the middle of a transaction).
Currently, Mango Markets/Solana’s block time stands closer to one second (for comparison, Ethereum’s average block time is thirteen seconds, and Bitcoin’s is closer to ten minutes – and has been even worse). Block time, essentially another name for network latency, is the amount of time it takes for a crypto miner to produce a new data file (or “block”) for a blockchain. However, despite Mango Markets’ speed, its block time does not compare with the high-speed cryptocurrency derivatives exchanges used by some professional investors, as can be seen in the graph below.

Who Is Behind Mango Markets?
All developments carried out on Mango Markets are sponsored by the Blockworks Foundation, a media brand dedicated to breaking news and delivering insights on the world of digital finance. Founded in 2018, Blockworks creates and distributes all manner of media content on crypto – from podcasts to newsletters – with over two million downloads a month.
In terms of Mango Markets’ foundation, both Coinmarketcap and Coingecko claim that Mango Markets was created by Maximilian Schneider and Daffy Durairaj, after the latter posted a margin trading mechanism on Solana. According to these websites, the pair later connected on the crypto forum Discord, and went on to found Mango Markets.
Strangely however, a Venezuelan man named Alejandro Betancourt also laid claim to founding Mango Markets as far back as 2017. This issue lacks clarity and leaves one with questions concerning the beginnings of Mango Markets.
The news that Betancourt’s Mango Markets was forced to halt operations shortly after its beginning, due to regulatory uncertainty surrounding DeFi in the country, partially answers some questions. However, the lack of clarity on Mango Markets foundation, both on its website and its litepaper make one lean toward caution.
What Is the Future for Mango Markets?
Mango Markets is currently in the process of developing Mango v3, the third version of their user interface. Designed to help inexperienced traders, and offer new advantages and options to professionals, Mango v3 will offer the following new features:
- Up to 16 different tokens to borrow, lend, or margin trade with on Serum DEX
- Up to 16 different perpetual contracts (PERP) with an initial leverage of up to 10x
- Plans to expand to 50+ markets and tokens after some anticipated Solana upgrades
- All token deposits and perpetual positions will be used as collateral by default
This upgrade means big things for Mango Markets and proves that there is still interest driving innovation at the platform’s highest levels. The move to trading sixteen different tokens through Serum DEX is a massive upgrade over the current five offered: BTC, ETH, SOL, SRM and MNGO. For any individual thinking of investing in Mango Markets’ burgeoning share of the market, Mango v3 may be seen as an indicator of future growth.
Mango Markets Price History and Analysis
Mango Markets is a relative newcomer in DeFi, launching in August and thus finding its way onto the market shortly after the 2021 crypto crash. Despite the crash, however, this was a period of growth, with a massive increase in the number of crypto users worldwide.
This timing clearly had a favorable effect on Mango Markets. During its initial 24-hour sale (ending Aug. 12th, 2021), Mango Markets raised over $70 million. When compared to usual goals of between $1-15 million, this shows an exceptional start to its life and proves the rising popularity of DeFi and Solana-based platforms.
Since launch, MNGO’s value has never dipped below the initial sale price of $0.23. In fact, despite a period where it returned to its original value, MNGO is currently worth almost double its initial cost, something it has achieved in just three short months.

Conclusion
With updates on the horizon, and a lack of serious competition due to unique offerings of low latency and even lower transaction fees, Mango Markets has quickly separated itself as a lead exchange on the already flourishing Solana blockchain. If the launch of Mango v3 goes ahead as intended, there is little reason to expect anything but a continued ascent from this rising star of decentralized cryptocurrency.
Mango Markets is an exciting new investment opportunity that is steadily growing in popularity. Moreover, with upgrades and improvements planned in the near future, it could rise in value soon too. However, there are two issues that should be weighed before investing large sums in MNGO. The first is that the company is new and thus only a small amount of data on Mango Markets is publicly available. The second is the lack of transparency surrounding the company, its formation, and how (and by whom) it was founded. Until these questions are answered in a satisfactory manner, it is probably advisable to tread with at least a modicum of caution.
Read More
- What is Solana: The Blockchain Aiming to Become the “Visa” of Crypto
- Phemex Analysis in A Minute: OM Surge 325% in 5 Days! What's Next?
- Phemex Analysis in A Minute: How to Trade SOLANA Like A Pro
- What is Monkey Ball Crypto: Monkey Ball NFT and MBS Token Explained
- Solana vs. Ethereum in 2025 and Beyond
- Phemex Analysis in a Minute: Is SOL Ready for a Breakout?
- What Is Serum: A Unique Decentralized Exchange on Solana
- July Crypto Market Analysis