Rocket Pool (RPL), sometimes referred to as Rocketpool, is the first DApp that lets its users take advantage of staking opportunities on Ethereum 2.0.
Ethereum’s gradual upgrade to a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain is opening up new opportunities in the world of decentralized apps (DApps). While the upgrade is expected to be finalized around early 2022, Ethereum has already introduced an interim PoS platform called Beacon Chain that runs in parallel with the main platform, Ethereum 1.0. By utilizing the PoS verification model, Beacon Chain allows participating nodes to earn crypto rewards by staking.
Rocket Pool’s native token, RPL, trades at around $32, with a total supply of 18 million tokens and a market cap of $582 million.

What Is Rocket Pool (RPL)?
Rocket Pool is a decentralized finance (DeFi) app providing opportunities to earn crypto rewards from staking on Ethereum 2.0. It is the first app of this nature. Users of the platform can earn staking rewards on Ethereum 2.0 without the need to satisfy the hefty financial requirements imposed on full verifier nodes.
What Is Staking and Delegated Staking?
Staking is the process by which nodes on a PoS blockchain verify the authenticity of transaction blocks, and earn cryptocurrency rewards for taking part in the verification. To set up a verifier node on a PoS platform, blockchain users must commit some computing hardware and crypto funds.
On Ethereum 2.0, the minimum requirements for a verifier node include committing at least 32 Ether (nearly $100,000). For many users, this is simply unaffordable.
Some blockchains, such as Tezos (XTZ) and Eos (EOS), allow delegation of staking, whereby any network user can delegate staking rights to a full verifier node by “lending” their crypto funds to the verifier. This delegated mode, usually, does not require users to commit large amounts of crypto funds. Unfortunately, Ethereum 2.0 does not allow delegated staking. That is where the Rocket Pool protocol comes into the picture.
Rocket Pool Staking
Rocket Pool has been in development with several beta versions since 2016, and is now ready for its mainnet launch on October 6. Users will be able to stake their crypto funds in ETH through the platform, and the protocol will manage the accrual and disbursement of the staking rewards. When you deposit your ETH to the protocol, you will receive rETH tokens, the protocol’s tokens used to secure your staking and accrue rewards.
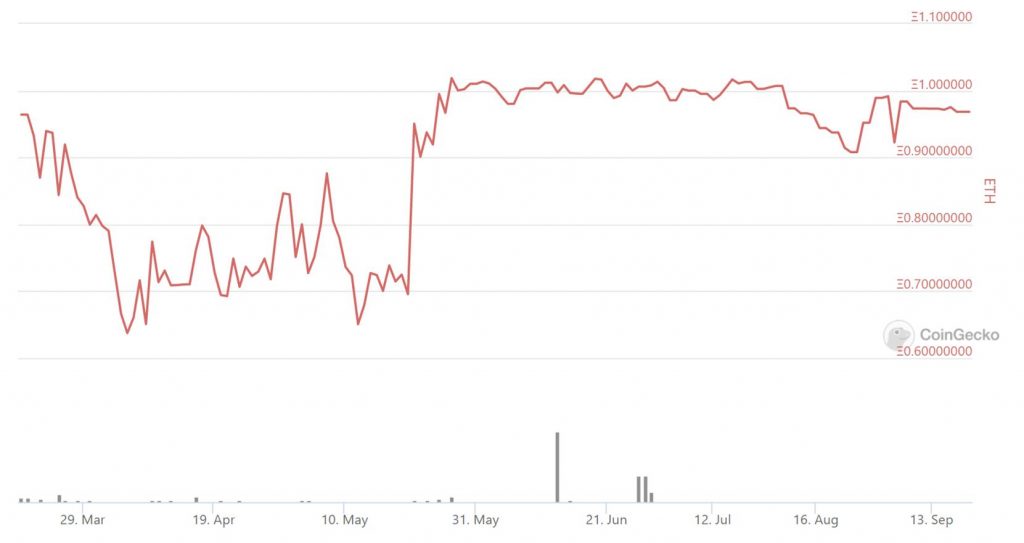
When you decide to unstake, you can swap your rETH, together with the accrued rewards, back to ETH. rETH is not pegged to ETH, but its swap rate to ETH has been remarkably stable in the last four months.
In addition to this affordable rETH-based staking, Rocket Pool also offers more sophisticated users a platform to function as a full staking node for Ethereum 2.0. This mode provides significantly more rewards than simple rETH staking.
One might wonder why a sophisticated blockchain user capable of acting as a verifier node needs to use Rocket Pool, when they can stake directly with Ethereum 2.0. First, Rocket Pool enables full node staking via its platform with only half of the usual funding requirements of Ethereum 2.0. While Ethereum asks for 32 Ether to be committed, Rocket Pool requires only 16 Ether. Additionally, verifier nodes can leverage Rocket Pool’s technical platform to quick-start their full node staking without the entire requisite technical setup.
How Does Rocket Pool Work?
Rocket Pool itself resides on Ethereum’s main blockchain, Ethereum 1.0. It accesses the new PoS Ethereum 2.0 blockchain, also known for now as the Beacon Chain, to carry out the staking operations.
The cross-platform access and interoperability is enabled via Oracle DAO, an important part of Rocket Pool’s architecture. Oracle DAO is essentially a number of nodes on the platform that have a responsibility to check transactions on the Beacon Chain and Ethereum 1.0 and signal the outcomes back and forth between the two networks.
The interoperability and transaction checking are based on a consensus mechanism whereby at least 50% of the Oracle nodes must confirm the authenticity of the transaction. At the genesis launch next month, Rocket Pool plans to have around 15 to 20 Oracle nodes. These important nodes will include the project’s peers in the blockchain community and ecosystem entrusted with the role of the initial Oracles. Oracle DAO will act in a completely decentralized and independent way from Rocket Pool.
Once the project is launched, new Oracle nodes may be added to the platform. The new nodes can join only by an invitation from an existing Oracle node, and by posting a “sizeable” RPL bond. Additionally, their candidature will need to be approved by at least 50% of the current nodes.
Rocket Pool uses a dual-token model for its functionality. The platform’s foundational token, RPL, is used for governance and as a transactional token for full node operators on the platform. The rETH token is used as a transactional token for staking and rewards accrual in the more affordable delegated staking format.
Who Is Behind Rocket Pool?
Rocket Pool was founded by Australian blockchain developer David Rugendyke in late 2016. The key motivation for the development of Rocket Pool was to democratize access to blockchain staking by making it available to a wider pool of users.
Rugendyke acts as the project’s CTO, while another experienced software engineer, Darren Langley, has recently become the project’s General Manager. Back in 2018, Langley had been one of the key developers working on the protocol.
Rocket Pool is based in Brisbane, Australia. The company raised an undisclosed amount of Venture Capital (VC) from a seed round in May 2018. So far, this has been Rocket Pool’s only VC funding. The funding came from ConsenSys Ventures, a VC arm of blockchain solutions development company ConsenSys.
RPL Coin Price History
Although Rocket Pool is launching in October, the project has been in active development and regularly released beta versions throughout the last 4 years. It minted and distributed RPL’s entire supply of 18 million tokens in late 2017.
Until April 2020, RPL’s trade volumes on exchanges were minimal. As the protocol’s final shape started to crystallize, RPL’s trading volumes took off. In April 2020, RPL was worth around $0.50. It then increased steadily and reached the $10 mark in March 2021. Riding on the back of the overall market bubble, RPL rose to a local peak of $23 by mid-May.

As the market bubble burst, RPL dropped to $8-$9 by July. Its decline during the burst was less severe than for many other crypto assets. Likewise, unlike many other cryptocurrencies that have not fully recovered from the bubble burst, RPL has been on a steep increase since July. It has now scaled the $30 heights, and trades at $32. These increases may well be driven by the pre-launch enthusiasm.
What Is the Future of Rocket Pool?
Since Rocket Pool will launch next month, it is difficult to make an assessment of the protocol’s future without the initial reaction from the market. The overall business concept of the project is very promising. It is also quite unique since there are no other platforms offering similar services as of now.
In that regard, Rocket Pool is poised for early success, capitalizing on its first-mover advantage. However, as Ethereum unfolds its PoS upgrade, more DApps similar to Rocket Pool are likely to hit the market. When these competitor platforms emerge, their presence will test Rocket Pool’s market viability.

Conclusion
Ethereum’s move to a complete PoS verification model creates opportunities for new DApp concepts. Rocket Pool has taken advantage of these opportunities and offers a unique way for a wide variety of users to earn rewards from Ethereum staking.
Since Ethereum 2.0 does not support delegated staking, Rocket Pool’s functionality democratizes access to staking by making it available to any interested user. You no longer need a hefty deposit or computing resources to become a staker on Ethereum.
Additionally, full node staking is also easier using Rocket Pool. While Ethereum requires 32 Ether to qualify as a verifier node, Rocket Pool has only a 16-Ether requirement. Moreover, the app lets you become a verifier node faster and with far less technical setup.
After four years of development and beta releases, Rocket Pool is ready for its mainnet launch on October 6, 2021. The protocol’s smart contract address is on Ethereum 1.0, where all the transactions with users of the protocol happen.
The actual staking will be carried out on Ethereum 2.0, and the interoperability between the two platforms is enabled via Oracle nodes, a group of 15 to 20 verifiers from Oracle DAO. Rocket Pool has stated that Oracle DAO acts in a decentralized manner and completely independently from the protocol itself.
A unique concept in itself, Rocket Pool is likely to achieve early success due to the first mover advantage. Rocket Pool’s business viability will only be thoroughly tested when similar apps emerge and the competition heats up.
Read More
- Ethereum 2.0 – Everything You Need to Know
- What is Staking: PoW vs. PoS Explained
- What Is A Crypto Launchpool and How To Earn Passive Income From It?
- What is a Liquidity Pool: Achieving Efficient Asset Trading
- What Are Decentralized Applications (dapps)?
- What is Sharding in Blockchain?
- What is Ethereum Casper and Why We Need It?
- What Does the DeFi Hype Mean for ETH?