Dai (sometimes erroneously referred to as Dai Coin) is a stablecoin; soft pegged to USD through automated smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Dai claims to be “the world’s first unbiased currency,” offering all the advantages of decentralization, with none of the volatility. Dai currently trades at $1.00 per coin with a supply of 3.2 billion, for a total market cap of $3.2 billion.

Dai vs. Other Cryptos
Dai differs significantly from the more established stablecoins such as Tether (USDT) and USDC. One key difference is that Dai is decentralized and trustless, meaning that holders don’t need to rely on any single controlling entity to keep the coin stable.
While other stablecoins tend to be backed by USD, Dai is generated, backed, and stabilized by “collateralized debt positions” (CDPs). These CDPs consist of a mix of other cryptocurrencies deposited into vaults on the Maker Protocol. Dai runs on an “over collateralized” lending system, meaning that every 1 Dai is backed by around 150% in collateral, depending on the associated token.

Source: TradingView
What make Dai a Stablecoin?
Dai is not generated through mining like BTC and ETH, nor is it minted according to the policy of a central entity like UDST. There is no hard limit on the amount of circulating Dai. As Dai is fundamentally tied to the CDPs backing it, the total supply is merely an indicator of the total collateral stored in its vaults at any given moment.
Once generated, Dai can be used to purchase goods, transferred, or staked in DeFi products just like any other Ethereum token. Unlike more traditional loans, Dai does not have any specific repayment period. Vaults remain active so long as enough collateral is put up to back the generated Dai.
When a loan and its accrued interest (known as the “stability fee”) is repaid in full, the Dai is automatically burned, and all collateral is made available for withdrawal. On the other hand, if the protocol determines that a vault has become too risky, that vault is automatically liquidated.
Dai’s price is controlled through a complex automated mechanism called the Target Rate Feedback Mechanism (TRFM) and an incentive structure. When Dai is worth over $1 USD, traders, known as “keepers,” are incentivized to sell Dai, which drives the price back to its target by increasing supply and lowering demand. Keepers can also profit when Dai’s price is lower than $1 USD by buying instead, reducing supply, which in turn increases demand and pushes the price back up.
Dai aims to remain stable even when the value of its collateralized tokens does not. For example, when the value of the collateralized token increases, the protocol marks the CDP as “safer” as the debt ratio has decreased. If the collateral value decreases, the CDP becomes “riskier” as the debt ratio has increased.
Suppose a CDP’s value ever drops so low that it can’t sustain the required collateralization ratio. In that case, the collateral is automatically sold off until the outstanding debt and liquidation penalty is sold off. This process is known as a collateral auction. Any Dai holder can profit by paying off the CDP through an auction system.
It follows that owners of risky CDPs are incentivized to pay off these debts to avoid automatic liquidation. Alternatively, an owner could make their CDP safer by paying down a portion of the debt as the collateral decreases in value. At any rate, the system encourages owners to handle their CDPs responsibly and penalizes those who don’t, all while protecting the overall Dai ecosystem.
Dai’s Governance
Dai’s proponents claim that unlike other stablecoins, its decentralized nature provides a more robust measure of reliability and trust. Tether, for example, came under a lot of scrutiny for its inability to prove its claim that every USDT was backed by $1 USD. This skepticism was vindicated in April 2019, when Tether Limited’s lawyers admitted that each USDT was backed by only $0.74 in cash and cash equivalents.
In comparison, all issuance and burning of Dai are publicly viewable on the Ethereum blockchain. And rather than a central entity, Dai is maintained by MakerDAO, a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) made up of holders of MKR tokens.
While anyone can submit a proposal to MakerDAO, only MKR holders can vote on key decisions regarding the administration and development of Dai and the Maker Protocol. Votes are allocated on a proportional basis, meaning that each MKR held provides one additional vote.
History of Dai and MakerDao
Dai was developed by MakerDAO, which was founded in 2015 by Rune Christensen, a Danish entrepreneur with a background in biochemistry and international business. In 2018, MakerDAO established the Maker Foundation to help bootstrap and manage the Dai ecosystem. Christensen was appointed as its CEO.
Dai was launched on the Ethereum network on Dec 1, 2017, on a single-collateral system backed by automated Ether smart contracts. Dai managed to remain very close to its price target of $1 USD during the first year of its existence, even when the value of the Ether backing its CDPs plummeted by roughly 80%.
On September 24, 2018, crypto investment firm Andreessen Horowitz invested $15 million USD into MakerDAO through the purchase of MKR tokens, representing around 6% of the total supply of MKR at the time.
In November of the same year, Dai moved from its original single-collateral system (now SAI) to its current status, the multi-collateral system (DAI). The first new token introduced for collateralization was the Basic Attention Token (BAT), followed by others such as USDC and Chainlink (LINK).
Controversy and Hurdles
The Dai project has not come without controversy, as reflected by the resignation of MakerDAO CTO Andy Milenius in an April 2019 open letter. In the letter, Milenius stated that Christensen had attempted to take full control over the DAO and that senior management was favoring traditional corporate efficiency over the DAO’s original goals.
Milenius claimed that these changes led to a breakdown in MakerDAO’s relationship with its developers, many of whom had moved to a separate firm, DappHub, to maintain their independence from management. MakerDAO COO Matt Richards soon fired back by arguing that Milenius did not represent the interests of MKR token holders and that “the project [would] likely be better off without [him].”
Dai experienced its biggest test in the March 2020 liquidity event. When the market crashed, skyrocketing gas prices rendered many DeFi products so expensive that they were nearly unusable. As the price of ETH plummeted, Dai instead moved in the other direction, peaking at roughly $1.10.
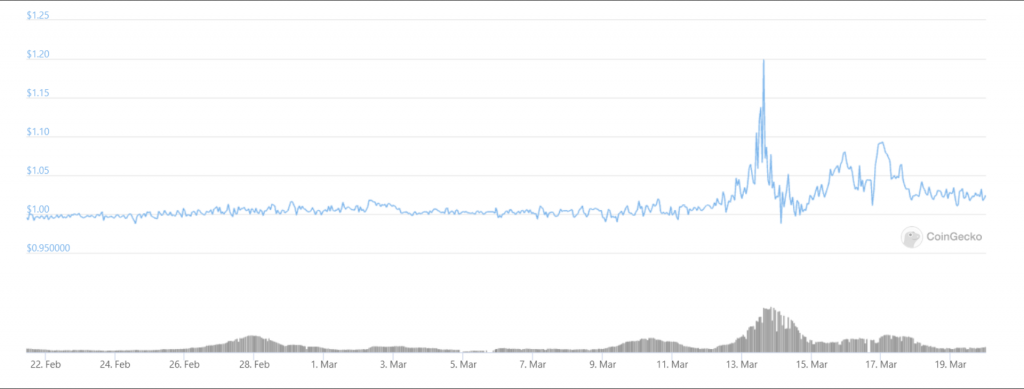
Source: CoinGecko
This was largely due to the fact that when ETH lost nearly 30% of its value in just 24 hours, many CDPs no longer held enough collateral to back the loan. To protect the Dai ecosystem, automated protocols liquidated roughly $4.5 million USD in loans.
While in normal market conditions, keepers would be incentivized to close out loans by bidding in collateral auctions, the prohibitively high gas prices disincentivized many from doing so. As a result, some participating keepers managed to win bids for up to 50 ETH in collateral by bidding close to 0 Dai.
Borrowers who hadn’t yet been hit rushed to close out their loans, only to find that very few Dai holders were willing to trade their stablecoins for other rapidly plummeting assets. The confluence of these conditions resulted in few new loans, meaning less Dai was being generated. With reduced supply and increased demand, the price of Dai started to rise.
The MakerDAO team responded to this looming crisis radically by allowing the use of USDC as collateral. The idea was that as USDC itself was a stablecoin backed by fiat currency stored in a bank account, it would serve as a stable option for Dai loans. By increasing supply, MakerDAO managed to nudge Dai’s price back down, but at the cost of increased centralization.
The Outlook for Dai
Dai’s proposition as a safeguard against inflation has led to incredible success in Latin America, especially Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and Argentina. In particular, concerns over hyperinflation in Argentina have made Dai its most popular cryptocurrency by volume, ahead of even BTC.
Dai is currently the world’s most popular stablecoin, and its composable nature means that it is incredibly easy to plug into most decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum platform. Dai continues to play an important role in popular DeFi platforms such as Compound and UniSwap.
Much like its competitor AAVE, Dai is known for serving as a strong safeguard for higher-volatility DeFi products. Holders of other currencies can first borrow Dai by storing collateral in vaults and then staking that borrowed Dai instead of the original coin.
MakerDao is also looking to expand Dai’s use to areas such as NFTs, where it has been integrated into a variety of art platforms such as the Museum of Contemporary Digital Art (MoCDA). E-commerce and payment systems are also where Dai has achieved some limited results through Coinbase Commerce and Dai-powered debit cards.
Conclusion
Future prospects for Dai will come down to its leading position in the DeFi space and continued adoption in regions facing unstable inflation. As long as the current trend of interest and growth in DeFi continues, Dai’s ease of application should ensure its continued popularity.
While Dai has shown resilience, investors interested in this “unbiased currency” should note its continued move towards further centralization, especially as more centralized coins become available for collateralization.
Read More
- All You Need to Know About Stablecoins: Cryptocurrency’s Gold Standard
- What Is DeFi: How To Be Your Own Bank With $100
- What is dYdX: An Order Book Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- Why Does Bitcoin Have Value?
- What is Aave: A Top DeFi Lending Platform
- What Are Decentralized Applications (dapps)?
- https://phemex.com/academy/defi
- What is Cryptocurrency & How It Differs From Digital Cash