In the evolving landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi), the architecture of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) has been a primary area of innovation. While the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model pioneered decentralized trading for the masses, it also introduced inherent challenges such as price slippage, impermanent loss, and vulnerability to Maximal Extractable Value (MEV). In response to these issues, a new generation of protocols has emerged. Among them is Hashflow, a decentralized exchange that utilizes a Request-for-Quote (RFQ) model to address the limitations of traditional AMMs.
Hashflow connects traders directly with professional market makers to provide firm, guaranteed price quotes. This approach aims to deliver a more efficient and secure trading experience by minimizing slippage and protecting users from front-running. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the Hashflow protocol, its native token HFT, its underlying technology, and its position within the competitive DeFi ecosystem.
Summary Box (Quick Facts)
-
Ticker Symbol: HFT
-
Chain: Ethereum
-
Contract Address (Ethereum): 0xb3999F658C0391d94A37f7FF328F3feC942BcADC
-
Circulating Supply: Approximately 581 Million HFT
-
Total Supply: 997.75 Million HFT
-
Primary Use Case: Governance, Staking, and participation in the Hashverse DAO
What Is Hashflow?
To understand what Hashflow is, it's essential to first understand the context of its creation. The majority of decentralized exchanges operate on an Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. AMMs rely on on-chain liquidity pools where prices are determined algorithmically based on the ratio of assets in the pool. While effective for enabling permissionless trading, this model has notable drawbacks, particularly for large-volume traders. These include:
-
Slippage: The execution price of a trade can differ significantly from the quoted price, especially for large orders that impact the asset ratio in the liquidity pool.
-
MEV (Maximal Extractable Value): Since all transactions are broadcast to a public mempool before confirmation, sophisticated bots can identify large trades and execute their own orders first to profit from the price impact, a practice known as front-running.
Hashflow explained simply: it is a decentralized exchange designed to mitigate these issues by replacing the AMM with a Request-for-Quote (RFQ) model. In this system, instead of interacting with a passive liquidity pool, a user’s trade request is sent to a network of professional market makers (PMMs). These PMMs compete to offer the best price for the trade. The user receives a cryptographically signed, guaranteed price quote that is immune to slippage.
Because the pricing process occurs off-chain, it is not visible in the public mempool, which provides strong protection against MEV attacks. The final settlement of the trade is then executed on-chain, preserving the security and self-custody benefits of decentralization. By integrating PMMs, Hashflow aims to bring institutional-grade liquidity and pricing efficiency to the DeFi space, offering all users access to deep liquidity with zero slippage.
How Many HFT Tokens Are There?
The economic design of a crypto project is defined by its tokenomics, and Hashflow’s HFT token was structured with specific goals for decentralization and long-term sustainability.
The total supply of HFT is fixed at 1 billion tokens, minted at the project's genesis. This fixed cap ensures that the token is not inflationary; no new HFT can be created. The circulating supply, however, increases over time according to a predetermined vesting schedule. This gradual release is intended to align the long-term incentives of the team, investors, and community members.
The initial distribution of the 1 billion HFT tokens was allocated to key stakeholders to foster a balanced and robust ecosystem. The philosophy behind the allocation was to ensure that the community and ecosystem partners would hold the majority of the supply, thereby decentralizing control over the protocol.
Here is the detailed breakdown of the HFT genesis supply:
-
Ecosystem Development (53.18% or 531,800,000 HFT): This is the largest allocation, designated for fostering protocol growth. It is subdivided to support various initiatives:
-
18.54% to Ecosystem Partners
-
13.08% to Community Rewards (including NFTs and exchange distributions)
-
7.50% for Designated Market Maker Loans to bootstrap liquidity
-
6.20% to Early Integration Partners
-
3.35% for Future Community Rewards
-
2.52% to Vendors and Early Service Providers
-
1.00% to the Community Treasury
-
1.00% for Hashverse Rewards
-
-
Early Investors (25% or 250,000,000 HFT): Allocated to the venture capital firms that provided the seed and Series A funding for the project's development.
-
Core Team (19.32% or 193,200,000 HFT): Reserved for the founding team and employees who designed and built the Hashflow protocol.
-
Future Hires (2.5% or 25,000,000 HFT): Set aside to attract and retain top talent for future development.
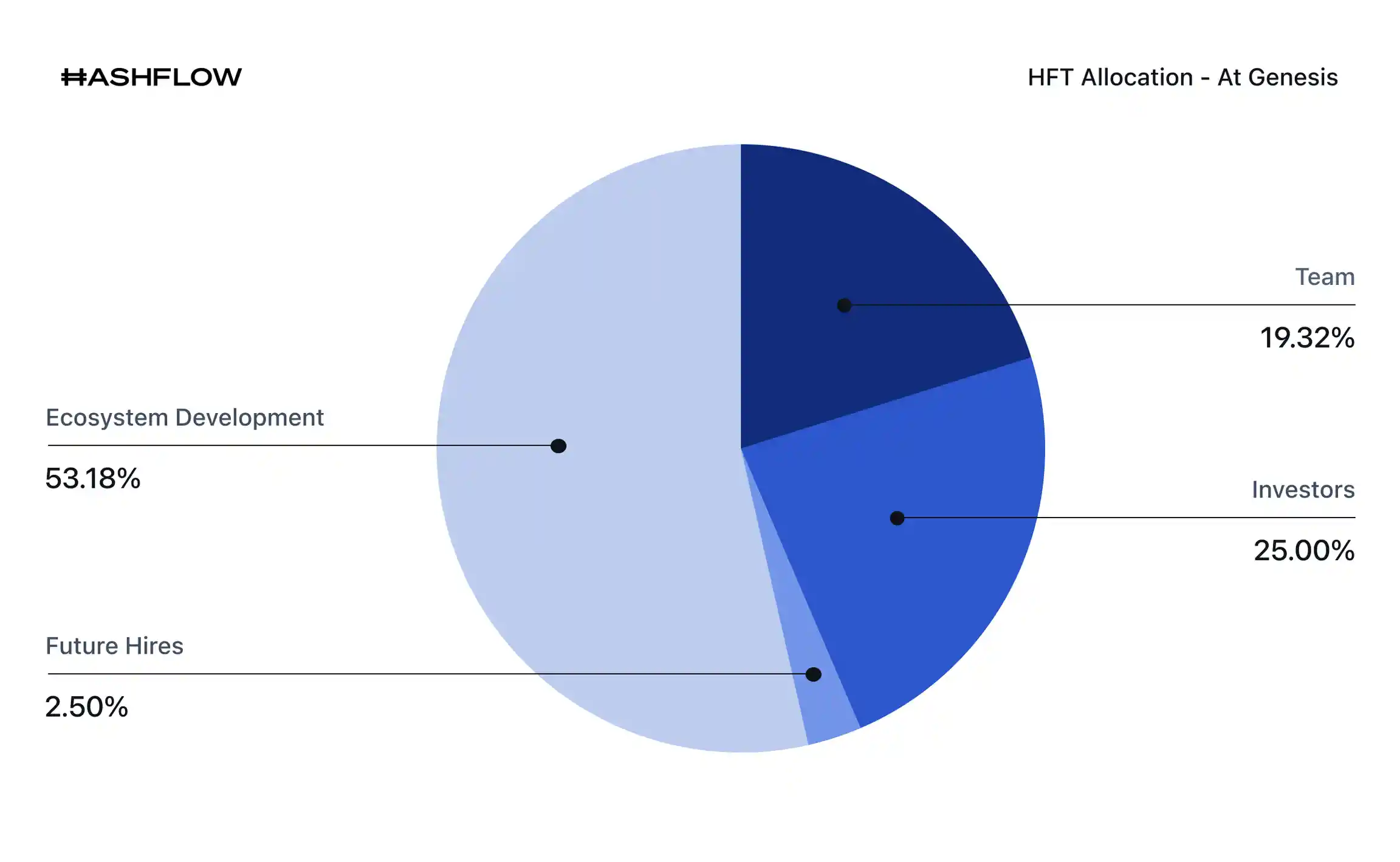
Both the Core Team and Early Investor allocations are subject to multi-year vesting schedules, ensuring a long-term commitment to the project's success and preventing significant sell-offs in the early stages. This structured distribution model is designed to support a gradual decentralization of the protocol while providing the necessary resources for its continued development and adoption.
What Does HFT Do? Examining the Token's Utility
The value of a utility token is derived from its function within its ecosystem. The HFT token serves a specific and critical purpose: it is the governance token for the Hashflow protocol and its gamified governance platform, The Hashverse.
The primary HFT use case is centered on governance through a vote-escrow (ve) token model. This model is designed to reward long-term commitment and align the interests of token holders with the health of the protocol.
Here’s how the utility of HFT functions:
-
Governance: Hashflow's governance is not based on simply holding tokens but on actively staking them. Users lock their HFT tokens to receive veHFT (Voting Escrow HFT). The amount of veHFT a user receives depends on two factors: the quantity of HFT staked and the duration of the lock-up period. A longer lock-up period grants a user proportionally more voting power. This system ensures that those with the most significant long-term stake in the protocol have the greatest influence over its future.
-
Protocol Management: Through the veHFT model, stakers gain the right to vote on key protocol parameters and strategic decisions. This includes proposals related to:
-
Protocol fees and revenue sharing mechanisms.
-
The deployment of funds from the community treasury.
-
Future development roadmaps and marketing initiatives.
-
The integration of new assets or market makers.
-
-
The Hashverse: Hashflow has implemented a gamified DAO interface known as The Hashverse. Staking HFT grants users access to this platform, where they can participate in governance, complete quests, and earn rewards. This approach is intended to increase user engagement and participation in the DAO, addressing the issue of voter apathy common in many DeFi projects.
In essence, HFT is the instrument that enables community ownership of the Hashflow protocol. It provides the mechanism for decentralized decision-making, ensuring that the platform evolves according to the collective will of its most committed users.
HFT vs. Uniswap: A Comparison of DEX Models
To better understand Hashflow’s position in the market, it is useful to compare it to Uniswap, the leading AMM-based decentralized exchange. While both facilitate on-chain swaps, their underlying technologies and trade-offs are fundamentally different.
| Feature | Hashflow (HFT) | Uniswap (UNI) |
| Core Technology | Request-for-Quote (RFQ): Off-chain price discovery with on-chain settlement. | Automated Market Maker (AMM): On-chain liquidity pools with algorithmic pricing. |
| Price Execution | Guaranteed Quotes: Offers zero slippage as the quoted price is cryptographically signed and fixed. | Subject to Slippage: Prices can vary between quote and execution, especially for large trades. |
| MEV Risk | Resistant: Off-chain quoting prevents front-running, as trade details are not public before execution. | Vulnerable: Public mempool exposure makes trades susceptible to MEV bots and front-running. |
| Capital Efficiency | High: Professional market makers can use complex, off-chain strategies to price assets efficiently. | Variable: Liquidity is often spread across a wide price range, with much of it being underutilized at any given time. |
| Cross-Chain Swaps | Native Integration: Supports bridgeless cross-chain swaps using market maker liquidity on different chains. | Requires External Bridges: Users must rely on third-party bridging protocols to move assets between chains. |
| Gas Fees | Gasless Option: Supports meta-transactions, where market makers can pay the gas fee on the user's behalf. | User-Paid Gas: Users are responsible for paying gas fees for every on-chain transaction. |
This comparison highlights that Hashflow and Uniswap are designed with different priorities. Uniswap excels at providing permissionless liquidity for a vast array of long-tail assets. Its strength lies in its open and accessible nature.
Hashflow, in contrast, is optimized for execution quality. By focusing on the RFQ model, it prioritizes price certainty, MEV protection, and capital efficiency, making it an attractive option for traders who value precision and cost-effectiveness, particularly for large-volume trades involving major crypto assets.
The Technology Behind Hashflow
Hashflow's performance is built on a sophisticated hybrid architecture that combines off-chain efficiency with on-chain security. The core components of its technology stack are designed to deliver a seamless and protected trading experience.
1. The Request-for-Quote (RFQ) Engine:
This is the central pillar of Hashflow's design. The trade lifecycle works as follows:
-
A user specifies a desired trade on the Hashflow interface.
-
This request is broadcast privately to a network of professional market makers.
-
These market makers, running advanced pricing models off-chain, compute and submit competitive price quotes. These models can incorporate data from centralized exchanges, their own inventory levels, and real-time volatility.
-
The Hashflow system presents the best quote to the user. This quote is a cryptographically signed message that guarantees the price and amount.
-
If the user accepts, the signed quote is submitted to the Hashflow smart contract on-chain, which validates the signature and executes the trade.
This model keeps the computationally intensive process of price discovery off-chain, resulting in faster quotes and lower overhead, while ensuring the final settlement remains trustless and secure on the blockchain.
2. Bridgeless Cross-Chain Swaps:
A significant technological differentiator for Hashflow is its native cross-chain swap functionality. Unlike traditional methods that require asset bridging—locking an asset on one chain to mint a wrapped version on another—Hashflow facilitates swaps directly. This is achieved by leveraging its network of market makers who maintain liquidity on multiple blockchains.
When a user wants to swap an asset on Chain A for an asset on Chain B, Hashflow coordinates the transaction with a market maker. The user sends their asset to the market maker's address on Chain A. Upon confirmation, the market maker releases the corresponding asset from their inventory to the user's address on Chain B. This process avoids the security risks and complexities associated with third-party bridges, offering a more streamlined and secure cross-chain experience.
3. MEV Protection and Gasless Swaps:
By design, the RFQ model provides inherent MEV resistance. Since trade intents and price quotes are handled off-chain and are cryptographically signed, MEV bots cannot see and exploit pending transactions in the public mempool. This protects users from value extraction via front-running.
Additionally, Hashflow supports meta-transactions. This feature allows market makers to bundle the gas fee into the quoted price and pay it on behalf of the user. For the end-user, this creates a "gasless" trading experience, simplifying the process and making transaction costs more predictable.
Team & Origins
The credibility of a project is often linked to the experience of its founding team. Hashflow was founded by Varun Kumar (CEO) and Victor Ionescu (CTO). Varun Kumar has a background in aerospace engineering and high-frequency trading, bringing deep expertise in building sophisticated quantitative trading systems. Victor Ionescu has extensive experience in software engineering and large-scale systems architecture, with past roles at major tech companies like Google and Facebook.
Hashflow emerged in 2021 and quickly garnered significant support from prominent venture capital firms. The project raised a $3.2 million seed round in April 2021 and followed up with a $25 million Series A round in October 2021. The list of investors includes industry leaders such as Dragonfly Capital, Electric Capital, Galaxy Digital, Coinbase Ventures, and Jump Crypto. This strong institutional backing provided the project with substantial resources and a high degree of credibility within the industry.
Key News & Events
Tracking a project's major milestones provides insight into its development and progress. Here are some key events in Hashflow's history:
-
April 2021: Hashflow secures $3.2 million in seed funding to begin protocol development.
-
October 2021: The project announces a $25 million Series A round, signaling strong institutional confidence.
-
August 2022: Hashflow launches its bridgeless cross-chain swap functionality, marking a major technological achievement.
-
November 7, 2022: The HFT token is launched, and The Hashverse governance platform is introduced. A retroactive airdrop distributes tokens to early platform users. To stay informed, users can follow news about HFT.
-
2023-Present: Hashflow continues its multi-chain expansion, deploying on major EVM-compatible networks like Arbitrum, Polygon, and BNB Chain to broaden its user base.
Analysis of HFT's Investment Potential
Evaluating the HFT investment potential requires a balanced analysis of its strengths and the challenges it faces in the competitive DeFi market. The HFT price is influenced by protocol adoption, overall market sentiment, and the perceived value of its governance rights.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. All investments in cryptocurrency are subject to high market risk. Please conduct your own research before investing.
Potential Strengths and Opportunities:
-
Technological Differentiation: The RFQ model's ability to offer zero-slippage trades and MEV resistance is a significant advantage over traditional AMMs, potentially attracting high-volume traders and institutions.
-
Cross-Chain Functionality: As the blockchain ecosystem becomes increasingly multi-chain, Hashflow's native and secure cross-chain swap feature could become a key driver of adoption.
-
Experienced Team and Strong Backing: The project is led by a team with relevant expertise in finance and technology and is supported by top-tier VCs, providing a solid foundation for growth.
-
Incentivized Governance: The veHFT model and The Hashverse are designed to foster an engaged community, which can lead to better governance decisions and a stronger network effect over time.
Potential Risks and Challenges:
-
Intense Competition: The DEX sector is highly competitive, with established players like Uniswap benefiting from massive liquidity and brand recognition. Gaining significant market share is a major challenge.
-
Dependence on Market Makers: The RFQ model relies on a network of active and competitive professional market makers. A decline in PMM participation could impact liquidity and pricing. This introduces a potential vector of centralization compared to fully permissionless AMMs.
-
Market Volatility: As with all altcoins, the value of HFT is highly susceptible to the volatility of the broader cryptocurrency market. A prolonged bear market could reduce trading volumes and, consequently, the value proposition of holding HFT for governance.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: The DeFi space continues to face an evolving and uncertain regulatory landscape. Future regulations targeting decentralized exchanges could impact Hashflow's operations and growth.
Conclusion:
Hashflow presents a compelling technological solution to well-known problems in decentralized trading. Its success will likely depend on its ability to leverage its unique advantages to capture a meaningful share of trading volume from established competitors. The HFT token's value is intrinsically linked to the protocol's adoption and the effectiveness of its governance model.
How to Buy HFT on Phemex
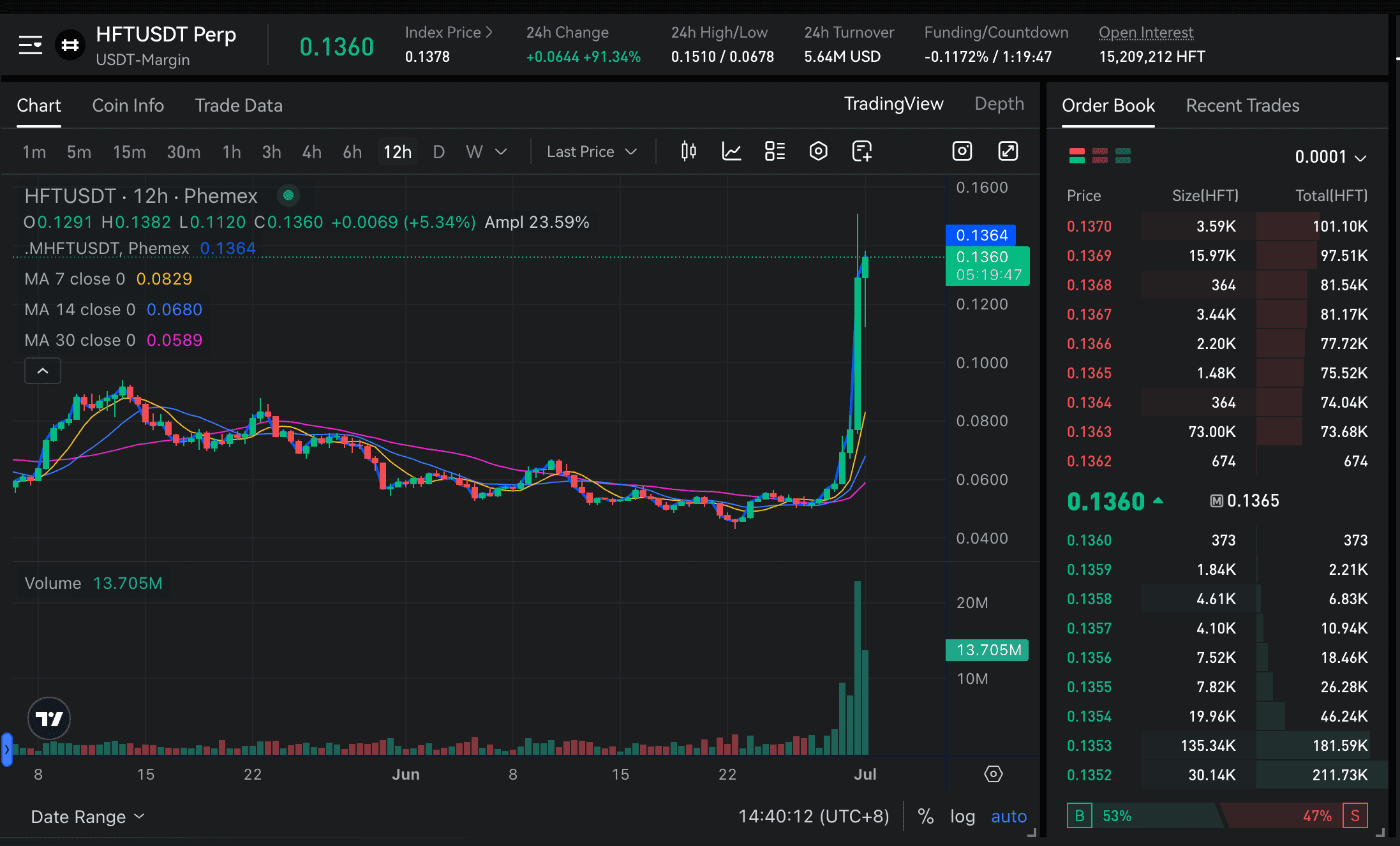
For those interested in acquiring HFT, you can trade HFT on a secure platform like Phemex, which offers both spot and futures trading for the token. If you are looking for information on how to buy HFT, follow these steps:
-
Register and Fund Your Phemex Account: Visit the Phemex website to create an account. You will need to complete the identity verification (KYC) process. After your account is verified, you can deposit funds, either by transferring existing cryptocurrency or by purchasing it directly with a credit/debit card.
-
Access the Spot Trading Interface: From the main dashboard, find the "Spot" tab in the top menu and click on "Spot Trading."
-
Locate the HFT Trading Pair: On the trading page, use the search bar (usually on the left) to type "HFT." Select the available trading pair, such as HFT/USDT, to open the corresponding market chart.
-
Execute Your Trade: You can now place an order to buy HFT. For immediate execution at the current market rate, use a "Market" order. Enter the amount of USDT you wish to spend, and the system will purchase HFT at the best available price. Alternatively, use a "Limit" order to specify the exact price at which you wish to buy.
-
Confirm and Store Your HFT: After your order is filled, the HFT tokens will be credited to your Phemex wallet. You can choose to hold them on the exchange for trading or withdraw them to a personal Web3 wallet to participate in The Hashverse.