Key Takeaways (Quick Facts)
-
Ticker Symbol: BDAG
-
Chain Architecture: Layer 1 Hybrid Blockchain/Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
-
Consensus: Proof-of-Work (PoW) combined with the PHANTOM GHOSTDAG protocol
-
Max Supply: 150 Billion BDAG
-
Primary Use Case: High-throughput, secure transactions, and EVM-compatible smart contracts for dApps.
-
EVM Compatible: Yes, allowing for easy migration of Ethereum-based dApps and tools.
-
Availability on Phemex: No (as of writing)
Introduction: A New Paradigm for Decentralized Ledgers
In the evolving world of cryptocurrency, developers continuously seek to solve the "Blockchain Trilemma"—the challenge of simultaneously achieving scalability, security, and decentralization. Traditional blockchains often have to compromise on one of these pillars to excel in the others. BlockDAG (BDAG) emerges as an ambitious project designed to overcome this limitation by fundamentally rethinking the structure of a decentralized ledger.
This guide from Phemex Academy provides a comprehensive explanation of BlockDAG. We will explore its innovative hybrid architecture, the sophisticated technology that powers it, its tokenomics, and the potential use cases it unlocks. For anyone looking to understand the next wave of blockchain innovation, this article offers crucial insights. Explore this guide to build your knowledge and make more informed decisions in the crypto market.
What Is BlockDAG (BDAG)? Explained for Beginners
At its core, BlockDAG is a Layer 1 protocol that merges the robust security of a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, famously used by Bitcoin, with the immense scalability and speed of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure.
To understand what makes BlockDAG unique, it's helpful to look at the two dominant models in crypto today:
-
The UTXO Model (like Bitcoin): The Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model treats value like digital cash. When you spend a UTXO, you use the whole amount and receive "change" back as a new UTXO. This model is highly secure and scalable for simple payments because transactions can be processed independently and in parallel.
-
The Account-Based Model (like Ethereum): This model works like a bank account, where balances are directly tied to user accounts. It excels at handling complex operations like smart contracts, which are the backbone of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and dApps.
BlockDAG’s innovation lies in its ability to support both models simultaneously. It offers a UTXO layer for fast, scalable payments and a separate, Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible subsystem for powerful smart contracts. A specialized bridge connects these two worlds, allowing developers and users to leverage the best features of each without compromise. This dual architecture is designed to create a versatile and powerful ecosystem for a wide range of applications.
How Many BDAG Coins Are There? A Look at the Tokenomics
A clear and well-structured tokenomics model is essential for the long-term health of any crypto project. BlockDAG has a maximum supply of 150 billion BDAG coins, with a transparent allocation plan designed to foster growth and reward participants.
BDAG Coin Allocation:
-
Presale (33.3%): 50 billion coins allocated to early supporters to fund development and build a strong initial community.
-
Miners (50%): 75 billion coins reserved as mining rewards. This large allocation is designed to incentivize miners to secure the network over the long term, with rewards following a geometrically reducing schedule.
-
Community & Ecosystem (12.7%): 19 billion coins dedicated to grants, partnerships, and community-building initiatives to fuel adoption and dApp development.
-
Liquidity (3.0%): 4.5 billion coins set aside to ensure sufficient liquidity on exchanges upon launch.
-
Team (1.0%): 1.5 billion coins for the core development team, a relatively small percentage that aligns their interests with the project's long-term success.
This distribution model heavily favors network security (miners) and early community growth (presale), reflecting a strategic approach to building a sustainable and decentralized ecosystem.
What Does BDAG Do? The Core Use Cases
The BDAG coin is the native utility token of the BlockDAG network, integral to its operation and economy. Its primary use cases include:
-
Transaction Fees: Users pay fees in BDAG for both UTXO payments and EVM-based smart contract interactions. The fee structure is designed to be competitive, with a target of around $0.01 per transaction initially.
-
Gas for Smart Contracts: Similar to Ethereum, executing smart contracts and dApps on BlockDAG’s EVM layer consumes "gas," which is priced and paid for in BDAG.
-
Mining Rewards: Miners who contribute their computational power to secure the network by validating transactions and creating new blocks are rewarded in BDAG.
-
Staking and Governance (Future): As the network matures, BDAG is expected to be used for staking and participating in governance decisions, allowing token holders to have a say in the future direction of the protocol.
The BlockDAG use case is inherently versatile, positioning the coin to capture value from both simple peer-to-peer payments and the rapidly growing DeFi and dApp markets.
BlockDAG vs. Bitcoin
| Feature | BlockDAG (BDAG) | Bitcoin (BTC) |
| Architecture | Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) | Linear Blockchain |
| Transaction Model | Hybrid (UTXO & Account-Based) | Purely UTXO-Based |
| Smart Contracts | Yes, fully EVM-compatible | Limited scripting capabilities |
| Scalability | High throughput via parallel processing | Low throughput (approx. 7 TPS) |
| Use Case | Versatile (payments, DeFi, dApps) | Primarily a store of value |
The key difference lies in architecture and purpose. While Bitcoin prioritizes security and decentralization for its role as digital gold, BlockDAG is built for a dynamic ecosystem of applications that require high speed and flexibility, without compromising on security.
The Technology Behind BlockDAG: A Technical Deep Dive
BlockDAG’s architecture represents a significant departure from traditional linear blockchains. Instead of a single chain of blocks where only one miner can add a block at a time, BlockDAG allows for a more fluid and parallel structure.
From Blockchain to Block-DAG
A conventional blockchain is a linear sequence of blocks. This structure is simple and secure but creates a bottleneck—every node must process every transaction in a strict order, limiting transaction throughput and driving up fees during periods of high demand.
BlockDAG replaces this linear chain with a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). In this structure, a new block can reference multiple previous blocks, not just one. This allows multiple blocks to be created and confirmed concurrently. Many transactions in the crypto world are unrelated (e.g., one person buying coffee while another swaps tokens in a different dApp), so there is no need to force them into a strict, single-file line. By ordering them in parallel, the network can achieve significantly higher transaction speeds.
The GHOSTDAG Protocol: Achieving Order in Chaos
Allowing parallel block creation introduces a new challenge: how does the network agree on a single, definitive transaction history and prevent double-spending? This is where BlockDAG’s consensus algorithm, a variation of the PHANTOM GHOSTDAG protocol, comes into play.
GHOSTDAG is a sophisticated tie-breaking algorithm that imposes a total order on the blocks within the DAG. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
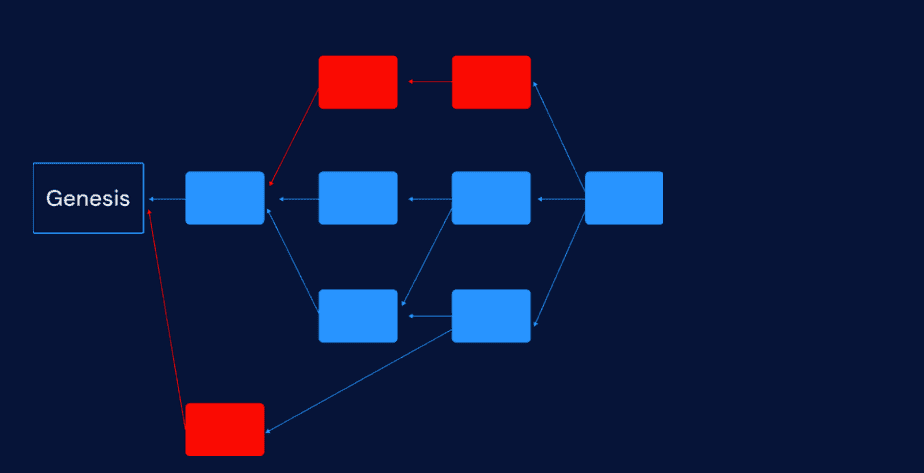
The blue-colored blocks in this figure form a k-cluster: each blue block is linked to all but at most k other blue blocks (here, k is 2). These blocks were produced (with high probability) by honest miners. The red blocks are only weakly connected to the blue blocks: they were produced by dishonest miners who did not follow the mining protocol.
-
Identifying Honest Blocks: The protocol analyzes the DAG’s structure. Blocks created by honest miners who are following the rules tend to be well-connected to the rest of the DAG. In contrast, blocks created by malicious actors (who might be trying to double-spend) are often poorly connected or "orphaned."
-
The "Blue" Set: GHOSTDAG identifies the largest and most well-connected set of blocks, referred to as the "blue" set. These are considered highly likely to have been mined by honest participants.
-
The "Red" Set: Any blocks outside this core group are labeled as "red" and are treated with suspicion.
-
Establishing Order: The protocol first orders the "blue" blocks. It then sorts the "red" blocks, giving priority to transactions within the blue set in case of a conflict.
This process ensures that even though blocks are produced in parallel, the network eventually reaches a secure and stable consensus on the transaction order. It effectively filters out malicious attempts by favoring the work of the honest majority, making the network highly resistant to attacks.
Full EVM Compatibility
A cornerstone of BlockDAG’s design is its full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This is a crucial feature for adoption and growth, as it means:
-
Easy dApp Migration: Developers can port existing Ethereum dApps and smart contracts to BlockDAG with minimal to no code changes.
-
Familiar Tooling: The network supports popular Ethereum development tools like MetaMask, Truffle, Remix, and Hardhat, lowering the barrier to entry for builders.
-
Standardized Tokens: BlockDAG supports established token standards like ERC-20 for fungible tokens and ERC-721 for NFTs.
This compatibility positions BlockDAG as a highly scalable alternative for developers looking to escape the high fees and congestion of the Ethereum network without having to learn an entirely new programming language or toolset.
The UTXO-EVM Bridge: Connecting Two Worlds
To make its dual-system seamless, BlockDAG implements a trustless bridge that allows its native currency, BDAG, to move between the UTXO and EVM domains. The exchange rate is fixed at 1:1. The process is carefully designed to prevent assets from being created or destroyed:
-
A user initiates a transfer from one domain to the other.
-
The coins on the source domain are destroyed or "burned."
-
A synchronization layer confirms that the burn is final.
-
Once confirmed, the asset management layer unlocks or "mints" an equivalent number of coins on the destination domain and assigns them to the user.
This mechanism ensures asset integrity while providing developers and users with the flexibility to choose the right system for their needs—whether it's a simple, fast payment or a complex smart contract interaction.
Team, Origins, and Governance
The BlockDAG project is supported by a public team and backed by a clear governance roadmap. Initially, a not-for-profit BlockDAG Foundation will oversee the ecosystem's development. The Foundation’s charter is to promote a transparent, inclusive, and decentralized global economy built on the BlockDAG ledger.
The long-term vision is to transition to a fully decentralized governance model where the community takes ownership of the protocol. This structured approach, combined with a public team, provides a level of transparency and accountability that helps build trust within the community.
Is BDAG a Good Investment? Assessing the Potential
Evaluating whether BlockDAG is a good investment requires a balanced look at its strengths and potential risks. This section is for informational purposes and is not financial advice.
Potential Strengths:
-
Innovative Technology: The hybrid PoW-DAG architecture is a genuinely novel approach to solving the blockchain trilemma. If successful, it could offer a significant performance advantage over existing blockchains.
-
Clear Tokenomics: The 150 billion max supply and well-defined allocation schedule provide predictability and show a long-term vision that rewards network participants.
-
EVM Compatibility: This feature is a powerful catalyst for adoption, as it allows BlockDAG to tap into the largest ecosystem of dApp developers and users in the crypto space.
-
Strong Presale Performance: The significant funds raised during the presale indicate strong early interest and provide the project with a substantial runway for development and marketing.
Potential Risks:
-
New and Unproven: As a new project, BlockDAG’s technology has yet to be tested at scale under real-world conditions. Its long-term stability and security remain to be proven.
-
Competition: The Layer 1 blockchain space is incredibly competitive, with established players like Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche commanding significant market share and network effects.
-
Market Volatility: Like all cryptocurrencies, the BDAG price will be subject to extreme market volatility. There is no guarantee of returns, and investors should be prepared for significant price swings.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: The global regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is still evolving and could pose challenges for new projects.
Conclusion: BlockDAG presents a compelling technological vision with significant investment potential. Its approach to scalability and flexibility is promising. However, investors should conduct their own thorough research, carefully consider the risks, and only invest what they can afford to lose.
How to Buy BDAG on Phemex
BlockDAG (BDAG) is not yet listed for trading on Phemex as of this writing. However, you can prepare for its potential launch by signing up for a Phemex account. By joining Phemex, you'll be ready to trade BDAG as soon as it becomes available and gain access to hundreds of other digital assets.
Stay tuned to Phemex announcements for the latest news on new coin listings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)?
A DAG is a data structure where information flows in one direction without cycles. In crypto, it allows for a network where multiple transaction blocks can be processed in parallel, rather than in a single sequential chain, leading to higher throughput.
2. How does BlockDAG prevent double-spending without a linear chain?
BlockDAG uses the GHOSTDAG protocol to analyze the relationships between all blocks in the DAG. The protocol identifies and prioritizes transactions from honest miners while discarding conflicting transactions from malicious actors, eventually establishing a single, universally agreed-upon transaction history.
3. Why is EVM compatibility so important?
EVM compatibility allows BlockDAG to seamlessly integrate with the largest and most active ecosystem of decentralized applications, developer tools, and users. This makes it easy for existing projects to migrate to BlockDAG and for new developers to start building without a steep learning curve.
4. How can I get the latest news about BlockDAG?
For the most current information and news about BlockDAG, it is best to follow the project's official website and community channels. For updates on potential listings and trading opportunities, keep an eye on Phemex's official announcements.
Stay ahead of the narratives. Trade the future on Phemex.