In the world of onchain finance, complexity is a double-edged sword. While it enables sophisticated strategies and novel financial products, it also creates significant operational burdens. Managing a dynamic portfolio, executing timely trades, and participating in complex governance often requires constant vigilance. The prevailing solution—manual intervention—is inefficient and prone to error. The alternative—granting automation tools direct access to private keys—is a security nightmare.
This challenge has given rise to a critical need for a new layer of digital infrastructure: a system that can automate complex onchain actions securely, reliably, and verifiably. This is the precise arena where Newton Protocol (NEWT) makes its entrance. It positions itself not as another DeFi application, but as a foundational protocol designed to be a verifiable automation layer for the entire onchain ecosystem.
Newton's ambition is to create a secure and decentralized framework where users can define and deploy "automation intents"—trigger-action programs that execute on their behalf without compromising security. This is a significant undertaking aimed at solving a core problem for power users, developers, and the next generation of onchain applications.
This in-depth guide will explore the architecture, tokenomics, and technical underpinnings of Newton Protocol, providing a clear and neutral overview of this ambitious project and its place in the evolving landscape of blockchain infrastructure.
Summary Box (Quick Facts)
-
Token Name / Ticker: NEWT
-
Contract Address: 0xd0ec028a3d21533fdd200838f39c85b03679285d
-
Blockchain: Ethereum (initially as an ERC-20)
-
Token Standard: ERC-20
-
Total Supply: 1,000,000,000 NEWT (fixed)
-
Primary Use Case: Securing the network via staking, paying for transaction fees, agent collateral, and governance.
-
Current Market Cap: Varies; check the latest NEWT price for real-time data.
-
Availability on Phemex: Coming soon
What Is Newton Protocol? An Explanation of Its Core Function
At its most fundamental level, Newton Protocol is a decentralized system designed to bring secure, verifiable automation to the blockchain. Its primary goal is to allow users to specify complex tasks that can be executed automatically by agents when certain conditions are met, all without handing over direct control of their funds.
To achieve this, the protocol is built on three core components:
-
Newton Model Registry: This is a canonical onchain registry where developers can publish "agent models." These models are essentially smart contracts that define a specific trigger-action logic (e.g., "IF this token's price drops by 10%, THEN execute this trade").
-
Newton Keystore: This is a specialized rollup (a Layer-2 scaling solution) designed specifically for storing and updating user permissions. Instead of giving an agent your private key, you grant it granular, revocable permissions via technologies like session keys or zkPermissions, which are securely managed by the Keystore.
-
Automation Intents: These are the instructions submitted by a user to the network. An intent links a user's wallet to a specific agent model in the registry and is governed by the permissions stored in the Keystore.
In practice, a user can find a trusted agent model, grant it permission to perform a narrow set of actions on their behalf, and then submit an intent. The Newton network, secured by validators, ensures that the agent executes the user's intent precisely as instructed and only within the cryptographic boundaries of its permissions. This creates a trust-minimized environment for sophisticated onchain automation.
The NEWT Token Supply: An Economic Blueprint
The economic design of a protocol is crucial for its long-term viability. Newton's tokenomics are structured around a fixed supply and a transparent distribution model aimed at aligning incentives across all ecosystem participants.
The total supply of NEWT is capped at 1,000,000,000 (one billion) tokens, with no inflationary mechanisms planned post-launch. This creates a predictable economic landscape.
The initial circulating supply at launch is set at 21.5% of the total. The project distinguishes between "Circulating Supply" (all unlocked tokens) and "Distributed Supply" (tokens actively claimed or deployed) to provide clearer insight into market dynamics.
The token allocation reflects a strong focus on ecosystem development:
-
Community Allocations (60%): The majority of tokens are earmarked for community-facing initiatives, including rewards for early adopters, network rewards for stakers, liquidity support, and dedicated funds for ecosystem growth, development, and foundation operations.
-
Internal Allocations (40%): This portion is allocated to Core Contributors, Early Backers, and Magic Labs, who were instrumental in the protocol's creation.
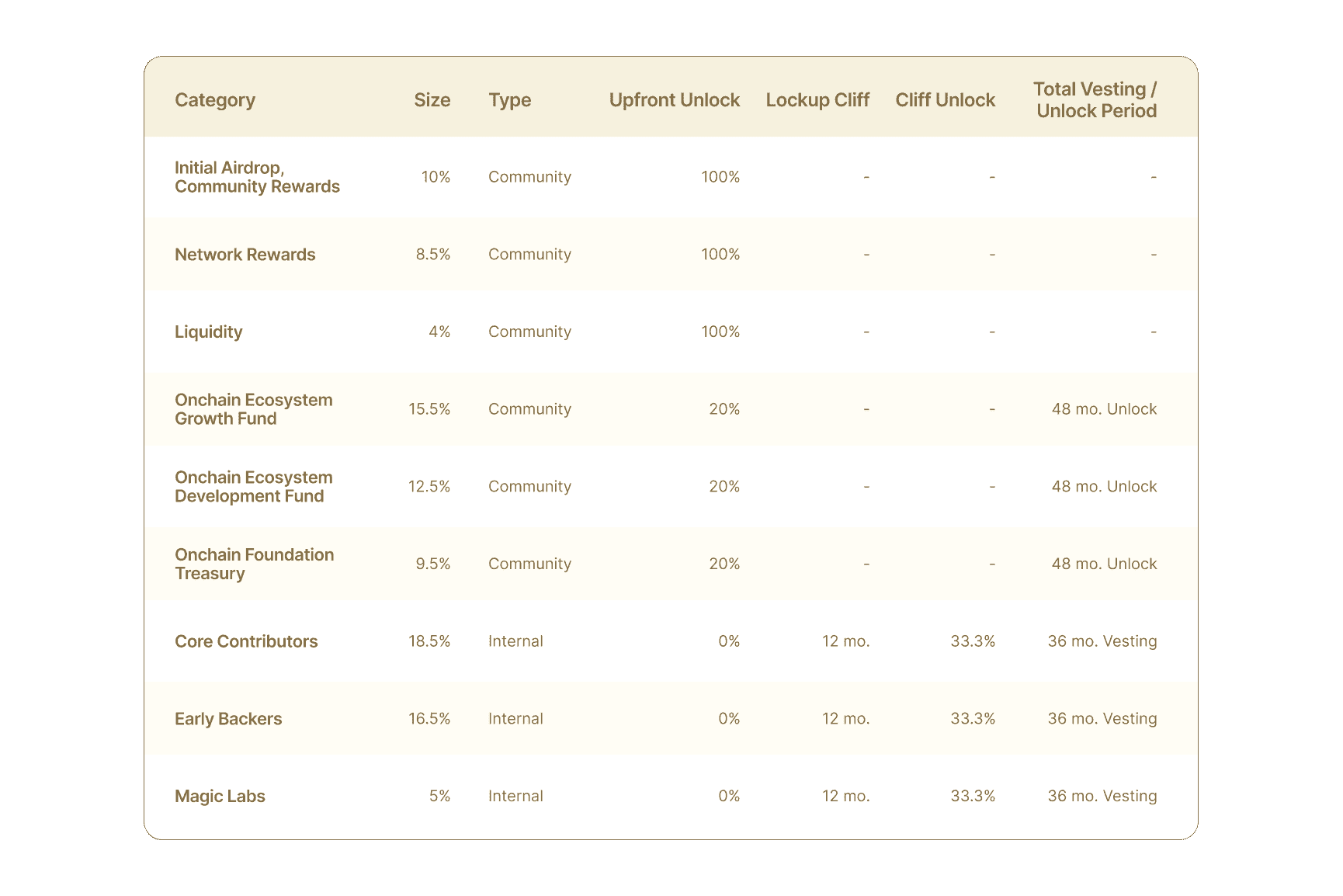
To foster long-term alignment, these internal allocations are subject to significant vesting periods: a 36-month vesting schedule with a 12-month initial lock-up (cliff). This ensures that the founding team and early supporters are incentivized to contribute to the protocol's success over an extended period. The large community-focused funds unlock linearly over 48 months, providing a sustained source of capital for ecosystem development.
What Does the NEWT Token Do? A Multi-Faceted Utility Model
The NEWT token is designed to be an integral part of the protocol, with its utility woven into the network's core functions. The primary NEWT use case can be understood through four key roles:
1. Staking for Protocol Security
The Newton Keystore rollup will operate on a delegated proof-of-stake (dPoS) consensus mechanism. NEWT is the asset used to secure this network. Participants can stake NEWT to act as validators or delegate their stake to a validator, contributing to the network's security and integrity. In return, they earn a share of protocol rewards.
2. Transaction Fees (Network Gas)
Once the Newton rollup is operational, NEWT will serve as its native gas token. Every action on the network—from executing an automation intent to issuing or updating permissions in the Keystore—will require a fee paid in NEWT.
3. Collateral for Agent Operators
A key innovation is the use of NEWT as collateral. For an operator to run an agent model from the registry and offer its services, they must stake NEWT. This stake acts as a security bond. If the agent misbehaves or fails validation, a portion of this collateral can be "slashed" (confiscated). This creates a powerful economic disincentive against faulty or malicious behavior, fostering a reliable marketplace of agents.
4. Protocol Governance
As the protocol decentralizes, staked NEWT will grant holders the ability to participate in governance. This includes voting on key protocol parameters, treasury disbursements, and other decisions that will guide the evolution of the ecosystem, placing control in the hands of its most committed users.
Newton Protocol vs. Ethereum: A Comparison of Purpose
Comparing Newton to a foundational blockchain like Ethereum helps clarify its specialized role. Newton is not an "Ethereum killer"; rather, it is a specialized Layer-2 solution that leverages Ethereum's security to perform a function that a general-purpose chain is not optimized for.
| Feature | Newton Protocol (NEWT) | Ethereum (ETH) |
| Core Purpose | A verifiable automation layer for onchain finance, focusing on secure agent execution. | A decentralized, general-purpose platform for smart contracts and a wide range of DApps. |
| Technology | A specialized "Keystore rollup" with delegated proof-of-stake (dPoS) consensus. | A monolithic proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain, scaling via general-purpose rollups. |
| Primary Focus | Enabling a secure onchain agent economy through trigger-action intents and granular permissions. | Hosting a diverse ecosystem including DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, and more. |
| Security Model | Inherits security from Ethereum for finality, while adding its own dPoS and economic security (slashing) for automation integrity. | The base layer of security for its entire ecosystem, secured by a large, decentralized validator set. |
Essentially, Ethereum provides the robust, decentralized court of final settlement, while Newton builds a specialized, high-performance industrial park on top of it, designed specifically for the business of onchain automation.
The Technology and Infrastructure Behind Newton
Newton's architecture is a composite of several advanced technologies designed to work in concert to provide secure automation.
Network Architecture & Core Components
As previously mentioned, the protocol's modular design separates intent definition (Model Registry), permission management (Keystore), and execution. This separation is key to its security model, as it ensures that an agent's capabilities are always constrained by the user's explicit, cryptographically-enforced permissions. The entire system is designed to be validated by a dPoS network, which ensures the integrity of automated actions.
Smart Contracts and Security Audits
The protocol is operated by a suite of smart contracts managing staking, permissions, and governance. The codebase for these components, including the token and airdrop contracts, has undergone third-party security audits from independent firms, with full reports available for public review. The core protocol components will be open-sourced, and further audits are planned as development progresses toward mainnet readiness.
Protocol Upgradeability
Newton employs a dual-layered upgrade model to balance flexibility with stability.
-
Governance-Controlled Parameters: Changes to economic variables like staking rewards or fee percentages can be modified via proposals and voting by staked NEWT holders.
-
Core Protocol Upgrades: Fundamental changes to the rollup logic or consensus mechanism are more rigorous. They require a hard fork, demanding explicit coordination and adoption by the network's validator operators, similar to how Ethereum itself upgrades. This prevents governance from making unilateral changes to the protocol's foundational layer.
Key Third-Party Dependencies
Newton integrates several cutting-edge technologies from the wider ecosystem to enable its functionality:
-
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): It leverages environments like Phala to run certain computational tasks in a confidential and verifiable manner.
-
Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Proof Systems: The protocol integrates with emerging zk-VM frameworks like Succinct and Risc Zero to enable its zk-permissioning model, allowing for verifiable offchain computation without revealing sensitive data.
Network Security and Staking Mechanics
Security is paramount for a protocol intended to automate financial transactions. Newton's approach is multi-pronged, combining cryptographic measures with economic incentives.
Staking and Slashing
Staking NEWT is the primary mechanism for securing the network. The protocol defines two main staking roles:
-
Validators: Stake NEWT to secure the Keystore rollup and earn protocol rewards for validating blocks and agent actions.
-
Agent Operators: Stake NEWT as collateral to run agent models. They earn fees from users but risk being slashed for misbehavior, with slashed funds being redistributed to affected users.
To ensure network stability, staked NEWT is subject to a 14-day unstaking (cool-down) period, during which the tokens are locked and non-transferable.
Rewards and Sustainability
Initially, staking rewards will be subsidized by the Foundation's "Network Rewards" allocation (8.5% of total supply) to bootstrap security. Over time, as protocol usage grows, a portion of the transaction fees paid in NEWT will be distributed to validators and stakers. This dual-rewards model is designed to transition the network from being foundation-subsidized to self-sustainable.
Validator Set Evolution
The network's decentralization will be a gradual process. It will begin with Foundation-controlled validators, transition to a permissioned set of third-party validators, and ultimately aim for a fully permissionless validator set, allowing broad participation.
Team and Origins
Newton Protocol's development is led by Magic Labs, with the Magic Newton Foundation established as a non-profit entity to support the long-term growth and decentralization of the ecosystem. This structure provides a clear separation between core development and community-focused stewardship, aiming to foster a robust and self-sustaining protocol over time.
Key Developments and Roadmap
The project's launch and future plans indicate a clear, phased approach to building out its vision.
-
Transparent Token Launch: The project launched with a detailed tokenomics plan, allocating 60% of the supply to community-oriented goals.
-
Phased Rollout: The roadmap involves the initial ERC-20 token launch, followed by the gradual implementation of the dPoS network and the Keystore rollup.
-
Upcoming Phemex Listing: The planned listing of NEWT on Phemex represents a significant step toward broader market access and liquidity. This will make it easier for interested participants to trade NEWT and learn how to buy NEWT on a major exchange.
Evaluating NEWT: Opportunities and Considerations
An assessment of Newton Protocol's potential requires a balanced view of its strengths and the inherent risks of such an ambitious project. Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. All investments in cryptocurrency carry significant risk.
Potential Strengths:
-
Addresses a Core Need: Secure onchain automation is a significant, unsolved problem. If Newton delivers a robust solution, it could become a critical piece of infrastructure for DeFi and beyond.
-
Structured Tokenomics: The fixed supply, long vesting schedules for insiders, and substantial community allocation create a strong economic foundation designed for long-term alignment.
-
Technical Sophistication: The protocol's use of TEEs, ZK-proofs, and a modular architecture demonstrates a deep understanding of the technical challenges involved.
Risks and Considerations:
-
Execution Risk: The project's vision is technically complex and ambitious. Its success is heavily dependent on the development team's ability to build, secure, and deploy the full Keystore rollup and its associated components.
-
Market Adoption: The protocol is building infrastructure for an emerging market. Its value will depend on developers building useful agent models and users adopting them at scale.
-
Dependency on Third-Party Tech: The protocol's reliance on external technologies like TEEs and zk-VMs means its performance and security are partially linked to the development and stability of those systems.
-
Competition and Market Dynamics: As the onchain automation narrative grows, Newton will likely face competition. Furthermore, the NEWT price will be subject to the volatility and macro trends of the broader crypto market.
Conclusion:
Newton Protocol is a technically ambitious project aiming to build foundational infrastructure for the future of onchain automation. It is not a simple application but a complex system designed to solve a difficult problem. Its success will hinge on flawless technical execution, widespread market adoption, and the robust security of its entire stack. For those interested in the infrastructure layer of the evolving web3 landscape, Newton represents a significant and noteworthy project to observe.







